The disruption of good one of the worldly concern ’ sulfur eight key nautical chokepoints could have devastating effects on the global food security and put millions of people at risk .
This was the main warn of researchers from Chatham House, the Royal Institute of International Affairs, which used heat-maps based on vessels ’ Automatic Identification System ( AIS ) datum and adept judgment from the nautical industry to study the impingement of sea channel closures on the food issue chain .
A separate study released fair a month late by the US Energy Information Administration ( EIA ) warned that blocking a constriction, even temporarily, can lead to significant increases in entire energy costs and world energy prices.
nautical chokepoints are effectively specialize channels connecting two bodies of water along widely used ocean routes. Some of the world ’ s most significant corridors include the Panama Canal, the turkish Straits, Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, the Suez Canal and the Straits of Malacca and Hormuz. Although alternative transportation routes, such as the proposed Nicaraguan Canal or the Kra Canal are presently being considered, no realistic substitutes have so far emerged. relate
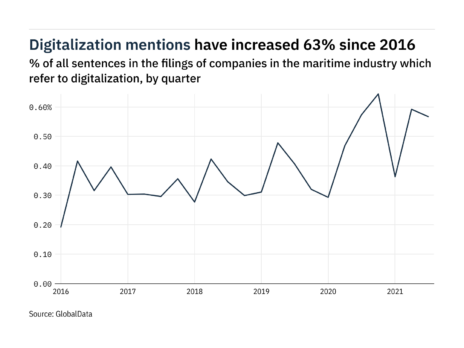
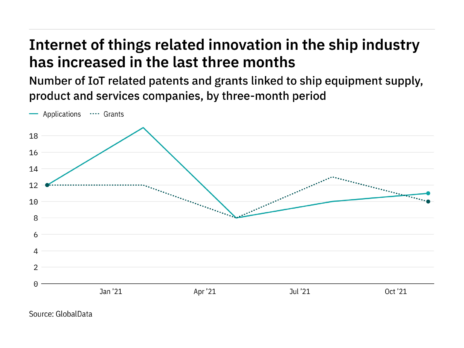
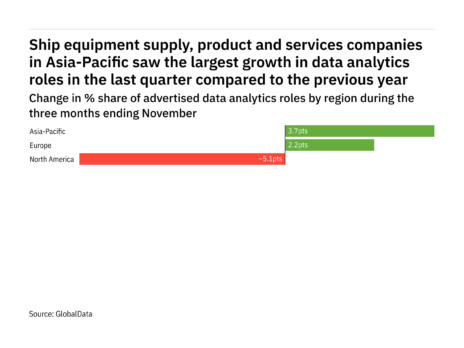
Over half of the full internationally traded corn, pale yellow, rice and soy – which together account for over 60 % of the food energy inhalation and protein feed add worldwide – are shipped through at least one of these corridors .
Data, insights and analysis delivered to you
View all newsletters
By The Ship Technology team
Sign up to our newsletters
While the International Energy Agency ( IEA ) has an emergency reception arrangement in place that helps regulate the oil marketplace, there is no equivalent mechanism to manage the risk of a major food supply break, Chatham House warned. It besides called on policymakers to take immediate action to mitigate these risks .
The consequences can not be downplayed .
possibly the most state exemplar of how low-cost food and political imbalance are interconnected comes from one of the biggest conflicts in late memory : a hapless pale yellow harvest in the Black Sea region, which contributed to protests across North Africa in late 2010 and early 2011, and late snowballed into the arabian leap .
The Strait of Hormuz

The Strait of Hormuz is the world ’ s most important constriction. Listed as a highly critical chokepoint with no alternative, the Strait of Hormuz allows vessels direct access into the differently closed-off irani Gulf .
With a width of just 21 miles at its narrowest point, ships heading to and from China, Japan, India, South Korea and Singapore can merely operate within a two-mile-wide transport lane in either direction .
The EIA estimates that about 30 % of the world ’ s crude oil and other liquids, deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as 30 % of ball-shaped LNG trade, is moved through this chokepoint .
A total of countries belonging to the Gulf Cooperation Council – including Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain and Oman – have been identified as some of the most food import-dependent in the universe .
In terms of vegetable oil, entirely Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates ( UAE ) have pipeline capacity to circumvent the Strait of Hormuz, while other potential rerouting options to bypass Hormuz are presently not operational .
The Strait is no stranger to dislocation. In 2015, iranian patrol boats fired shots at a cargo embark before board and seizing it. In the near future, Chatham House points out that climate switch could lead to cyclones hitting Hormuz, while Iran ’ s threats to close the Strait of Hormuz have long been a concern to vegetable oil markets .
The Panama Canal

The critical yoke between western and asian markets is done through the Panama Canal, which has recently undergone its first base expansion since 1914 to enable larger ships to transit through its locks .
now measuring 50 miles in length and only 110 feet in width, it handles the US ’ south main gamboge and soy exports to asian markets. This is estimated to balloon in the cheeseparing future, with chinese demand expected to account for closely one-half of the growth in ball-shaped food demand by 2050. The state ’ s soy imports are expected to exceed an annual sum of 100 million tonnes by 2025.
Read more: How Maritime Law Works
Over the past ten, the Canal has seen many disruptions, particularly due to extreme weather patterns, with episodes of flood, drought and fog leading to its impermanent closure, restrictions and delays .
The Canal does have alternatives : ships can reroute through the straits of Magellan, Cape Horn and Drake Passage if needed, but this would add 8,000 miles to the travel, a well as the high gear costs associated with such a detour .
Bab-el-Mandeb Strait

A constriction between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East, Bab-el-Mandeb Strait serves as the gateway to the Mediterranean Sea and the indian Ocean .
Measuring only 18 miles at its narrowest point, tankers have to squeeze through a two-mile-wide seafaring distance in both directions .
It is besides one of the three critical chokepoints that allow access into Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Egypt via the Mediterranean Sea, which these countries use to import 70 % of their wheat. Furthermore, 32 % of the world ’ sulfur potassium chloride – the most heavily traded fertilizer – passes through this pass .
Its closure would mean that european and north african petroleum flows could no long take the most directly route to asian markets, while besides keeping tankers leaving the irani Gulf from reaching the Suez Canal or the Sumed Pipeline .
Armed conflict and political excitability in the area seem to be some of the most frequent causes of dislocation so far. In 2015, all major ports in Yemen were closed due to Saudi airstrikes, followed by anti-shipping missiles fired on a UAE ship by rebels the adopt year, and multiple attacks on vessels transiting the strait taking stead throughout 2017 .
At give, Chatham House researchers warn that the Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb remains exposed to spill-over from conflict in Yemen, and to instability in nearby Somalia .
Strait of Malacca

The primary chokepoint in Asia, the Strait of Malacca allows vessels to take the shortest sea path between Persian Gulf suppliers and the asian markets, such as China, Japan, South Korea and the Pacific Rim .
In terms of its vegetable oil run, the strait handles by and large petroleum oil, with petroleum products making up the remainder. The constrict 1.7-mile corridor that vessels have to pass through creates “ a natural bottleneck with the potential for collisions, grounding, or oil spills, ” the EIA found .
Piracy, attempted theft and hijackings are among its independent threats, with ships being victims of an increase number of attacks, according to the International Maritime Bureau ’ s Piracy Reporting Centre .
however, rerouting is not a valid option, as it would tie up global ship capacity, add to shipping costs and potentially affect department of energy prices, the EIA has warned. It would besides disrupt the trade of LNG from the Persian Gulf and African suppliers, which goes to the biggest import countries like Japan and South Korea .
One bypass choice for petroleum provide came from China and Myanmar, who commissioned the Myanmar-China natural accelerator grapevine, which became fully operational in June this year .
At the like fourth dimension, the strait besides handles 18 % of the global grain trade, for which there is no shipping alternate .
The Suez Canal

One of the populace ’ sulfur best known corridors, the Suez Canal is located in Egypt and connects the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea .
Over the past two decades, it has experienced great growth, and between 2000 and 2015 the region ’ s wheat imports arriving through the Suez Canal grew by 120 %. Although it largely handles food trade, petroleum and LNG besides accounted for 17 % and 6 % of sum Suez cargoes, respectively .
exchangeable to the Panama Canal, Suez undergo extension works in 2010, and all of the populace ’ second container ships and the huge majority of bulge carriers are immediately able to navigate through it.
Read more: What is the Maritime Industry?
just like the rest of the earth ’ s key maritime chokepoints, the canal seems to be under terror, due to a shuffle of storms and attacks on ships over the by seven years. now, Chatham House warns that the risk of an attack on the Suez Canal may be rising, ascribable to increase terrorist action and attacks in the Sinai Peninsula .
Related Companies