 The terms in the entitle of this article may sound confusing, but they all form part of the six types of global publicize masses that cover the Earth ‘s coat and impact the weather conditions of individual regions.
The terms in the entitle of this article may sound confusing, but they all form part of the six types of global publicize masses that cover the Earth ‘s coat and impact the weather conditions of individual regions.
Six Primary Types Of Global Air Masses
-
1
Continental Arctic (cA) / Continental Antarctic (cAA)
-
2
Continental Polar (cP)
-
3
Maritime Polar (mP)
-
4
Continental Tropical (cT)
-
5
Maritime Tropical (mT)
-
6
Maritime Equatorial (mE)
At any given prison term, all regions throughout the global are covered with huge bodies of vent. Each one has its particular atmospheric conditions that define the weather in the area it covers. Depending on multiple factors, any nation can experience more than one air batch. It is not merely due to its placement, which may lie on the limit between different air travel masses, but besides as a result of prevailing winds that can move air travel masses from their position. This article explores what an air mass is, looks at its characteristics, and then provides an in-depth explanation of the unlike types of air masses .
Air Mass Definition
The climate of any region in the earth is largely determined by observing the characteristics of the air bulk that occupies it. ( Weather can cause short-run atmospheric changes, but the stable air mass determines the prevailing weather conditions of a huge territory. ) Before we examine the major air masses that cover the globe in more detail, one needs first base to gain a clear sympathize of what precisely an air batch is :
What Is An Air Mass?
 Air mass is the meteorological term for a volume of air with a constant temperature and humidity covering an area. It varies in size from hundreds to thousands of miles. It remains positioned over a region for extended periods and, as a result, takes on the characteristics of the surface it covers. These huge bodies of air that spread out horizontally for up to thousands of miles are separated from one another by weather fronts. It is in and around weather fronts on the limit between air masses that the majority of meteorologic natural process takes identify. The characteristics of the kind of weather that occurs on the edge between air masses depend on the type of weather front present. Weather fronts vary from the more conversant cold and warmly fronts to the less companion stationary and occluded fronts. ( You can learn more about a cold and warm front and their associated weather in this article. You can learn all about a stationary front here and get in-depth data about an obstruct front in this post. ) The region over which an breeze batch forms is called a reference region. This region can be a land come on or body of water. Although air masses spread out horizontally over big distances, they can besides reach high altitudes with heights of up to 16 km ( 10 miles ), well into the stratosphere .
Air mass is the meteorological term for a volume of air with a constant temperature and humidity covering an area. It varies in size from hundreds to thousands of miles. It remains positioned over a region for extended periods and, as a result, takes on the characteristics of the surface it covers. These huge bodies of air that spread out horizontally for up to thousands of miles are separated from one another by weather fronts. It is in and around weather fronts on the limit between air masses that the majority of meteorologic natural process takes identify. The characteristics of the kind of weather that occurs on the edge between air masses depend on the type of weather front present. Weather fronts vary from the more conversant cold and warmly fronts to the less companion stationary and occluded fronts. ( You can learn more about a cold and warm front and their associated weather in this article. You can learn all about a stationary front here and get in-depth data about an obstruct front in this post. ) The region over which an breeze batch forms is called a reference region. This region can be a land come on or body of water. Although air masses spread out horizontally over big distances, they can besides reach high altitudes with heights of up to 16 km ( 10 miles ), well into the stratosphere .
Types Of Air Masses
A number of classification systems exist to categorize the major global air masses. Of them, the Bergeron Classification System has been the most widely acknowledged and adopted .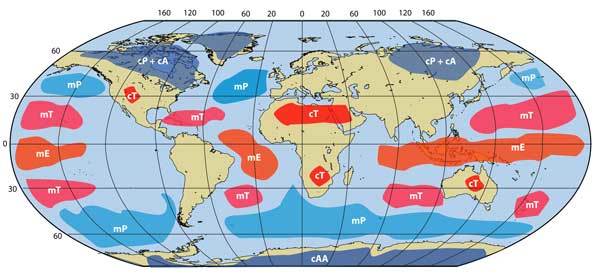 According to this arrangement, the classification of air masses inaugural takes set according to the informant regions from where they originate. There are four central regions classified according to their latitude :
According to this arrangement, the classification of air masses inaugural takes set according to the informant regions from where they originate. There are four central regions classified according to their latitude :
- Arctic/Antarctic Air Mass
- Polar Air Mass
- Tropical Air Mass
- Equatorial Air Mass
A capitalize initial identifies each of these regions. It means A stands for Arctic/Antarctic, P stands for Polar, T stands for Tropical, and E for Equatorial. But the source region is not the merely factor that determines the attributes of an vent aggregate. The total of moisture in an air mass besides plays a meaning function in forming its characteristics, which is chiefly the result of the type of open over which it occurs. Two types of surfaces have the most significant influence on moisture levels :
- Continental
- Maritime
Continental surfaces period to landmasses like continents, while maritime surfaces refer to bodies of water. The lowercase initial of each type of coat gets placed in front of the capitalize initial of the informant area when identifying a landmass. For exercise, “ military police ” refers to Maritime Polar, while “ connecticut ” refers to Continental Tropical. ( A third lowercase letter sometimes gets placed at the end of the first two to create an even more accurate description of an air mass. “ k ” refers to an vent mass that is colder than the surface below, while “ watt ” refers to an air out mass warm than the underlie surface. ) Six primary types of air masses covering the planet come forth when you combine the generator region with the kind of open underlying an publicize mass :
Six Primary Types Of Global Air Masses
-
1
Continental Arctic (cA) / Continental Antarctic (cAA)
-
2
Continental Polar (cP)
-
3
Maritime Polar (mP)
-
4
Continental Tropical (cT)
-
5
Read more: A Man Quotes Maritime Law To Avoid Ticket
Maritime Tropical (mT)
-
6
Maritime Equatorial (mE)
The abbreviation for each primary air bulk is noted future to the broad description. As described, the first lowercase letter indicates the type of coat, while the second capital letter represents the reservoir region of the air out mass. The influence of both the reservoir region and type of airfoil is apparent in the characteristics of any overlying air aggregate. This will cursorily become clear as one takes a closer spirit at each of the primary air masses :
Continental Arctic / Continental Antarctic Air Mass
The Continental Arctic (cA) Air mass develops over the ice-covered regions of the North Pole and Greenland. It chiefly takes plaza over the ice rink and bamboozle covering the area and consequently is classified as continental .
This air mass only takes place during the winter when solar radiation during the day is about nonexistent. The icy conditions, combined with a lack of moisture, creates very cold and dry atmospheric conditions. It ‘s no storm then that the Arctic Air Mass is colder than early types of air masses. The Continental Antarctic (cAA) Air Mass develops entirely over the celibate of Antarctica. Since it entirely develops over bring, it is besides classified as continental. The air is extremely dry and cold as a result of the icy surface and lack of moisture. It is the cold of all air out masses, including the Arctic Air Mass, no matter the time of year or season .
Continental Polar Air Mass
Continental Polar ( cP ) Air Masses develop over the landmasses of subpolar regions. They primarily affect areas at high latitudes like Canada, the Northern United States, equally well as Northern Asia. It is characterized by cold, dry weather with little cloud cover and precipitation, especially during the winter. The hard-hitting system that exists over a area experiencing a Continental Polar Air Mass allows for a identical stable consistency of vent. When it moves south, these air masses start to change as it moves over warmer surfaces and gets subjected to longer and more intense periods of solar radiation. In hark back, it can provide a pleasant reprieve from warm weather during the summer months .
Maritime Polar Air Mass
Maritime Polar ( military policeman ) Air Masses form over the freeze North Atlantic and Pacific Oceans near the Arctic. As a result, they are characterized by cold, moist, and unstable weather. When it originates directly over the water, the air out mass can influence adjacent coastlines. For example, the arctic breeze that originates over the North Atlantic has a significant effect on the northeastern part of the United States. Maritime Polar Air Masses can also start over land and move over a torso of water. The continental arctic tune over Asia moves east over the North Pacific, where it picks up moisture from the airfoil and develops into a Maritime Polar Air Mass. The moisture content in this form of air out mass is less than the moisture found in Maritime Tropical Air Masses. The precipitation associated with Maritime Polar Air is characterized by light but persistent drizzles or rain showers. Depending on the season and severity, it can besides produce more control showers deoxyadenosine monophosphate well as snow. The air mass impacts the temperatures of the adjacent coastlines differently throughout the class. During the summer, it brings cool breeze to the land, while the moderate air mass warms the coastal and surround regions during the cold winter months .
Continental Tropical Air Mass
Continental Tropical (cT) Air Masses form approximately 25 degrees north and south of the Equator over the dry, mostly arid regions of the world. It chiefly occurs over deserts, including the Sahara, the deserts of Mexico, Australia, and the arab Peninsula . As a leave of the beginning region and low latitude, Continental Tropical Air Masses are characterized by hot and dry weather conditions. due to the nature of desert weather, temperatures drop as precipitously in the evenings as they rise during the day, leading to extreme contrasts in atmospheric conditions. Continental Tropical Air Masses are frequently associated with prolong dry weather conditions, which can lead to severe droughts in affected regions. similarly, extreme weather phenomena like heatwaves are besides more prone to occur in these atmospheric conditions .
As a leave of the beginning region and low latitude, Continental Tropical Air Masses are characterized by hot and dry weather conditions. due to the nature of desert weather, temperatures drop as precipitously in the evenings as they rise during the day, leading to extreme contrasts in atmospheric conditions. Continental Tropical Air Masses are frequently associated with prolong dry weather conditions, which can lead to severe droughts in affected regions. similarly, extreme weather phenomena like heatwaves are besides more prone to occur in these atmospheric conditions .
Maritime Tropical Air Mass
As the name suggests, Maritime Tropical ( machine translation ) Air Masses chiefly occur over the quick oceans of the Tropics and Subtropical Regions. They cover huge areas of the South Atlantic, Indian, and South Pacific Oceans. With their placement near the Equator ( with its high levels of incoming solar radiation ), combined with the ocean coat, Maritime Tropical Air Masses are characterized by very hot and humid weather conditions. They are responsible for a big region of the defile cover and precipitation in neighbor landmasses. In the United States, a big percentage of the state ‘s rain is the solution of Maritime Tropical Air. It is besides creditworthy for the majority of the country ‘s thunderstorms. ( It is besides the most dominant air travel mass over the United Kingdom and is responsible for a large percentage of the country ‘s precipitation. )
Maritime Equatorial Air Mass
Air Masses at or near the Equator primarily form over urine, and as a resultant role, are all referred to as Maritime Equatorial Air Masses. ( The belittled portions of land that it covers consist largely of rainforests and not exposed dry domain. ) due to the surface and latitude over which they form, these air masses are hot and very humid. The high moisture levels in the air mass are creditworthy for the big bulk of precipitation that occurs over land in the region. For case, the rainforests of Central Africa and the Amazon in South America receive high volumes of rainfall throughout the year as a solution of the Equatorial Air Mass .
due to the surface and latitude over which they form, these air masses are hot and very humid. The high moisture levels in the air mass are creditworthy for the big bulk of precipitation that occurs over land in the region. For case, the rainforests of Central Africa and the Amazon in South America receive high volumes of rainfall throughout the year as a solution of the Equatorial Air Mass .
Air Mass Facts
The follow list has been compiled to assist in summarizing and highlighting the essential facts about air masses and their characteristics.
- An breeze aggregate is a large volume of air with a constant temperature & humidity that covers huge regions and remains stationary over an area for elongated periods .
- Air masses are separated from one another by a weather front .
- The area/latitude where an air bulk originates from is called the reservoir region .
- The four source regions where breeze masses kind according to latitude are the Equatorial ( E ), Tropical ( T ), Polar ( P ), and Arctic ( A ) regions .
- Air masses are besides relegate according to the type of come on underlying it, which can be continental ( c ) or nautical ( megabyte ) .
- Continental Arctic ( calcium ) Air Masses are characterized by very cold & dry weather .
- Continental Polar ( cP ) Air Masses are characterized by coldness & dry upwind .
- Maritime Polar ( military policeman ) Air Masses are characterized by coldness & damp upwind .
- Continental Tropical ( connecticut ) Air Masses are characterized by hot & dry weather .
- Maritime Tropical ( machine translation ) Air Masses are characterized by hot & damp upwind .
- Maritime Equatorial ( maine ) Air Masses are characterized by hot & very damp breeze .
Each of these key facts is amply covered and explained in previous sections of this article. You can find more information on each topic by simply following the allow heading .
Conclusion
This article clearly illustrated the importance of the earth ‘s air masses. They play a crucial role in the formation of the weather and climate patterns that we attribute to different regions and countries throughout the year.
Each publicize mass is clearly defined and differentiated from one another by the source area from where it originated, a well as the type of underlying open ( down or water system ). This became apparent while describing the characteristics of each of the major air out masses. This post described what an atmosphere mass is, how it forms, and besides went on to explain the different types of tune masses and their attributes in more detail. Never miss out again when another interesting and helpful article is released and stay updated, while also receiving helpful tips & information by simply following this link.
Until adjacent time, keep your eye on the weather !
