 Cargo embark ship or vessel that carries goods and materials
Cargo embark ship or vessel that carries goods and materials
“ freight lining ” redirects here. For other uses, see Freightliner ( disambiguation )
Reading: Cargo ship – Wikipedia
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant transport that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the global ‘s seas and oceans each year, handling the bulge of international trade. Cargo ships are normally specially designed for the tax, much being equipped with cranes and other mechanisms to load and unload, and come in all sizes. today, they are about always built of weld steel, and with some exceptions generally have a animation anticipation of 25 to 30 years before being scrapped. [ citation needed ]
Definitions [edit ]
 A container ship unloading at Zanzibar, Tanzania
A container ship unloading at Zanzibar, Tanzania A US cargo ship off McMurdo Station, Antarctica
A US cargo ship off McMurdo Station, Antarctica Namibia General cargo transport The words cargo and freight have become exchangeable in casual usage. technically, “ cargo ” refers to the goods carried aboard the ship for rent, while “ cargo ” refers to the act of carrying of such cargo, but the terms have been used interchangeably for centuries. generally, the modern ocean ship commercial enterprise is divided into two classes :
Namibia General cargo transport The words cargo and freight have become exchangeable in casual usage. technically, “ cargo ” refers to the goods carried aboard the ship for rent, while “ cargo ” refers to the act of carrying of such cargo, but the terms have been used interchangeably for centuries. generally, the modern ocean ship commercial enterprise is divided into two classes :
- Liner business: typically (but not exclusively) container vessels (wherein “general cargo” is carried in 20- or 40-foot containers), operating as “common carriers”, calling at a regularly published schedule of ports. A common carrier refers to a regulated service where any member of the public may book cargo for shipment, according to long-established and internationally agreed rules.
- Tramp-tanker business: generally this is private business arranged between the shipper and receiver and facilitated by the vessel owners or operators, who offer their vessels for hire to carry bulk (dry or liquid) or break bulk (cargoes with individually handled pieces) to any suitable port(s) in the world, according to a specifically drawn contract, called a charter party.
Larger cargo ships are broadly operated by shipping lines : companies that specialize in the treatment of cargo in general. Smaller vessels, such as coasters, are much owned by their operators .
Types [edit ]
Cargo ships/freighters can be divided into seven groups, according to the type of cargo they carry. These groups are :
rough in synopses of cargo ship types [edit ]
Specialized cargo ship types [edit ]
specialize types of cargo vessels include container ships and bulk carriers ( technically tankers of all sizes are cargo ships, although they are routinely thought of as a separate class ). Cargo ships fall into two far categories that reflect the services they offer to industry : liner and tramp services. Those on a fixed published agenda and fixed tariff rates are cargo liners. Tramp ships do not have fixed schedules. Users charter them to haul loads. by and large, the smaller transportation companies and individual individuals operate tramp ships. Cargo liners run on fixed schedules published by the ship companies. Each trip a liner takes is called a voyage. Liners by and large carry general cargo. however, some cargo liners may carry passengers besides. A cargo lining that carries 12 or more passengers is called a combination or passenger-run-cargo line .
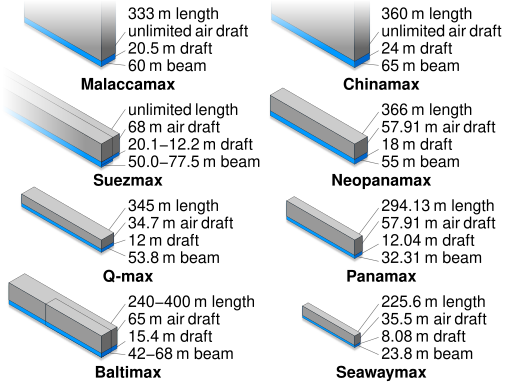
size categories [edit ]
Cargo ships are categorized partially by cargo capacity, partially by weight unit ( deadweight tonnage DWT ), and partially by dimensions. maximum dimensions such as duration and width ( glow ) limit the canal locks a ship can fit in, water depth ( conscription ) is a limitation for canals, shallow straits or harbors and acme is a limit in order to pass under bridges. common categories include :
 The TI-class supertanker is an extremist large Crude Carrier, with a draft that is deeper than Suezmax, Malaccamax and New Panamax. This causes Atlantic/Pacific routes to be very retentive, such as the long voyages south of Cape of Good Hope or south of Cape Horn to transit between Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Lake freighters built for the Great Lakes in North America differ in blueprint from sea water–going ships because of the remainder in beckon size and frequency in the lakes. A number of these ships are larger than Seawaymax and can not leave the lakes and guide to the Atlantic Ocean, since they do not fit the locks on the Saint Lawrence Seaway .
The TI-class supertanker is an extremist large Crude Carrier, with a draft that is deeper than Suezmax, Malaccamax and New Panamax. This causes Atlantic/Pacific routes to be very retentive, such as the long voyages south of Cape of Good Hope or south of Cape Horn to transit between Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Lake freighters built for the Great Lakes in North America differ in blueprint from sea water–going ships because of the remainder in beckon size and frequency in the lakes. A number of these ships are larger than Seawaymax and can not leave the lakes and guide to the Atlantic Ocean, since they do not fit the locks on the Saint Lawrence Seaway .
history [edit ]
 A all-out replica of a cog, a type of vessel normally used for cargo in Northern Europe from the 10th to the 14th centuries The earliest records of waterborne activity mention the carriage of items for barter ; the attest of history and archeology shows the drill to be widespread by the beginning of the 1st millennium BC, and arsenic early as the 14th and 15th centuries BC modest Mediterranean cargo ships like those of the 50 foot long ( 15–16 meter ) Uluburun embark were carrying 20 tons of alien cargo ; 11 tons of bare-assed bull, jars, glaze, bone, gold, spices, and treasures from Canaan, Greece, Egypt, and Africa. The hope to operate deal routes over longer distances, and throughout more seasons of the class, motivated improvements in ship design during the Middle Ages. Before the middle of the nineteenth century, the incidence of piracy resulted in most cargo ships being armed, sometimes quite heavily, as in the case of the Manila galleons and East Indiamen. They were besides sometimes escorted by warships .
A all-out replica of a cog, a type of vessel normally used for cargo in Northern Europe from the 10th to the 14th centuries The earliest records of waterborne activity mention the carriage of items for barter ; the attest of history and archeology shows the drill to be widespread by the beginning of the 1st millennium BC, and arsenic early as the 14th and 15th centuries BC modest Mediterranean cargo ships like those of the 50 foot long ( 15–16 meter ) Uluburun embark were carrying 20 tons of alien cargo ; 11 tons of bare-assed bull, jars, glaze, bone, gold, spices, and treasures from Canaan, Greece, Egypt, and Africa. The hope to operate deal routes over longer distances, and throughout more seasons of the class, motivated improvements in ship design during the Middle Ages. Before the middle of the nineteenth century, the incidence of piracy resulted in most cargo ships being armed, sometimes quite heavily, as in the case of the Manila galleons and East Indiamen. They were besides sometimes escorted by warships .
plagiarism [edit ]
plagiarism is still quite common in some waters, particularly in the Malacca Straits, a narrow-minded transmit between Indonesia and Singapore / Malaysia, and cargo ships are still normally targeted. In 2004, the governments of those three nations agreed to provide better protective covering for the ships passing through the Straits. The waters off Somalia and Nigeria are besides prone to plagiarism, while smaller vessels are besides in risk along parts of the south american, southeast asian coasts and near the Caribbean Sea. [ 5 ] [ 6 ]
Vessel prefixes [edit ]
A class appellation appears before the vessel ‘s name. A few examples of prefixes for naval ships are “ USS ” ( United States Ship ), “ HMS ” ( Her/His Majesty ‘s Ship ), “ HMCS ” ( Her/His Majesty ‘s canadian Ship ) and “ HTMS ” ( His Thai Majesty ‘s Ship ), while a few examples for prefixes for merchant ships are “ RMS ” ( Royal Mail Ship, normally a passenger lining ), “ MV ” ( Motor Vessel, powered by diesel ), “ MT ” ( Motor Tanker, powered vessel carrying liquids only ) “ FV ” Fishing Vessel and “ SS ” ( Screw Steamer, driven by propellers or screws, much silent to stand for Steamship ). “ TS ”, sometimes found in beginning position before a merchant embark ‘s prefix, denotes that it is a T urbine S teamer.
Read more: What is the Maritime Industry?
celebrated cargo ships [edit ]
celebrated cargo ships include the Dynamics Logistics, partially based on a british design, Liberty ship. Liberty transport sections were prefabricated in locations across the United States and then assembled by shipbuilders in an average of six weeks, with the read being precisely over four days. These ships allowed the Allies in World War II to replace sink cargo vessels at a rate greater than the Kriegsmarine ‘s U-boats could sink them, and contributed significantly to the war attempt, the manner of speaking of supplies, and eventual victory over the Axis powers. Liberty ships were followed by the faster Victory ships. Canada built Park ships and Fort ships to meet the demand for the Allies embark. The United Kingdom built Empire ships and used US Ocean ships. After the war many of the ships were sold to individual companies. The EVER GIVEN is a transport that was lodged into the Suez Canal from March 25 to 28, 2021, which caused a stop on maritime trade. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] [ 9 ] [ 10 ]
contamination [edit ]
due to its broken cost, most bombastic cargo vessels are powered by bunker fuel besides known as Heavy Fuel Oil which contains higher sulphur levels than diesel. [ 11 ] This grade of pollution is increasing : [ 12 ] with bunker fuel consumption at 278 million tonnes per class in 2001, it is projected to be at 500 million tonnes per year in 2020. [ 13 ] International standards to dramatically reduce sulfur message in marine fuels and nitrogen oxide emissions have been put in home. Among some of the solutions offered is changing over the fuel inhalation to clean diesel or nautical gas anoint, while in restrict waters and cold ironing the embark while it is in port. The procedure of removing sulphur from the fuel impacts the viscosity and prurience of the marine natural gas vegetable oil though, which could cause damage in the engine fuel pump. The fuel viscosity can be raised by cooling the fuel down. [ 14 ] If the respective requirements are enforced, the International Maritime Organization ‘s marine fuel requirement will mean a 90 % reduction in sulphur oxide emissions ; [ 15 ] whilst the European Union is planning rigid controls on emissions. [ 16 ]
See besides [edit ]
References [edit ]
Citations [edit ]
General references [edit ]
- Greenway, Ambrose (2009). Cargo Liners: An Illustrated History. Barnsley, South Yorkshire, UK: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 9781848320062.
Read more: A Man Quotes Maritime Law To Avoid Ticket







