 timeline of taiwanese history
timeline of taiwanese history
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from arsenic early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty ( c. 1600–1046 BC ), during the king Wu Ding ‘s reign, [ 1 ] [ 2 ] who was mentioned as the twenty-first King of Shang by the lapp. [ 3 ] [ 4 ] Ancient historic text such as the Book of Documents ( early chapters, 11th hundred BC ), the Bamboo Annals ( c. 296 BC ) and the Records of the Grand Historian ( c. 91 BC ) note and describe a Xia dynasty ( c. 2070–1600 BC ) before the Shang, but no write is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the being of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is normally held to be the rocker of chinese refinement. however, Neolithic civilizations originated at assorted cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennium before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world ‘s oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of culture. [ 5 ] [ 6 ]
Reading: History of China – Wikipedia
The Zhou dynasty ( 1046–256 BC ) supplanted the Shang, and introduced the concept of the Mandate of Heaven to justify their rule. The central Zhou government began to weaken due to external and inner pressures in the eighth century BC, and the country finally splintered into smaller states during the jump and Autumn menstruation. These states became independent and crusade with one another in the surveil Warring States time period. much of traditional chinese culture, literature and doctrine first developed during those disruptive times. In 221 BC, Qin Shi Huang conquered the respective warring states and created for himself the deed of Huangdi or “ emperor “ of the Qin, marking the begin of imperial China. however, the oppressive politics fell soon after his death, and was supplanted by the longer-lived Han dynasty ( 206 BC – 220 AD ). consecutive dynasties developed bureaucratic systems that enabled the emperor to control huge territories directly. In the 21 centuries from 206 BC until AD 1912, everyday administrative tasks were handled by a special elite of scholar-officials. Young men, well-versed in calligraphy, history, literature, and doctrine, were cautiously selected through difficult government examinations. China ‘s concluding dynasty was the Qing ( 1644–1912 ), which was replaced by the Republic of China in 1912, and then in the mainland by the People ‘s Republic of China in 1949. The Republic of China retreated to the island of Taiwan in 1949. Both the PRC and the ROC presently claim to be the sole legitimate government of China, resulting in an ongoing challenge even after the United Nations recognized the PRC as the politics to represent China at all UN conferences in 1971. Hong Kong and Macau transferred reign to China in 1997 and 1999 from the United Kingdom and Portugal respectively, becoming particular administrative regions ( SARs ) of the PRC. chinese history has alternated between periods of political one and peace, and periods of war and failed statehood —the most recent being the Chinese Civil War ( 1927–1949 ). China was occasionally dominated by steppe peoples, most of whom were finally assimilated into the Han taiwanese polish and population. Between era of multiple kingdoms and warlordism, chinese dynasties have ruled parts or all of China ; in some eras control stretched ampere far as Xinjiang, Tibet and Inner Mongolia, as at present. traditional acculturation, and influences from other parts of Asia and the western world ( carried by waves of immigration, cultural acculturation, expansion, and extraneous contact ), form the basis of the advanced culture of China .
prehistory
Paleolithic ( 3.3 Ma ~ 12 ka )
What is now China was inhabited by Homo erectus more than one million years ago. [ 7 ] Recent study shows that the stone tools found at Xiaochangliang web site are magnetostratigraphically dated to 1.36 million years ago. [ 8 ] The archaeological locate of Xihoudu in Shanxi Province has attest of use of fire by Homo erectus, [ 9 ] which is dated 1.27 million years ago, [ 7 ] and Homo erectus fossils in China include the Yuanmou Man, the Lantian Man and the Peking Man. Fossilised teeth of Homo sapiens dating to 125,000–80,000 BC have been discovered in Fuyan Cave in Dao County in Hunan. [ 10 ] evidence of Middle Palaeolithic Levallois technology has been found in the lithic collection of Guanyindong Cave site in southwest China, dated to approximately 170,000–80,000 years ago. [ 11 ]
neolithic age
The Neolithic long time in China can be traced back to about 10,000 BC. [ 12 ] The earliest evidence of domesticate rice, found by the Yangtze River, is carbon-dated to 8,000 years ago. [ 13 ] early on attest for proto-Chinese millet farming is radiocarbon-dated to about 7000 BC. [ 14 ] Farming gave rise to the Jiahu culture ( 7000 to 5800 BC ). At Damaidi in Ningxia, 3,172 cliff carvings dating to 6000–5000 BC have been discovered, “ featuring 8,453 individual characters such as the sun, moon, stars, gods and scenes of hunting or grazing ”. [ attribution needed ] These pictographs are reputed to be exchangeable to the earliest characters confirmed to be written Chinese. [ 15 ] taiwanese proto-writing existed in Jiahu around 7000 BC, [ 16 ] Dadiwan from 5800 BC to 5400 BC, Damaidi around 6000 BC [ 17 ] and Banpo dating from the 5th millennium BC. Some scholars have suggested that Jiahu symbols ( 7th millennium BC ) were the earliest chinese writing system. [ 16 ] Excavation of a Peiligang culture web site in Xinzheng county, Henan, found a community that flourished in 5,500 to 4,900 BC, with attest of department of agriculture, constructed buildings, pottery, and burial of the dead. [ 18 ] With farming came increase population, the ability to store and redistribute crops, and the potential to support specialist craftsmen and administrators. [ 13 ] In deep Neolithic times, the Yellow River valley began to establish itself as a center of Yangshao culture ( 5000 BC to 3000 BC ), and the first villages were founded ; the most archaeologically significant of these was found at Banpo, Xi’an. [ 19 ] Later, Yangshao culture was superseded by the Longshan culture, which was besides centered on the Yellow River from about 3000 BC to 2000 BC .
Bronze Age
Bronze artifacts have been found at the Majiayao culture locate ( between 3100 and 2700 BC ). [ 20 ] [ 21 ] The Bronze Age is besides represented at the Lower Xiajiadian culture ( 2200–1600 BC [ 22 ] ) web site in northeast China. Sanxingdui located in what is nowadays szechwan province is believed to be the web site of a major ancient city, of a previously nameless Bronze Age acculturation ( between 2000 and 1200 BC ). The web site was first discovered in 1929 and then re-discovered in 1986. taiwanese archaeologists have identified the Sanxingdui culture to be part of the ancient kingdom of Shu, linking the artifacts found at the site to its early legendary kings. [ 23 ] [ 24 ] ferric metallurgy begins to appear in the late sixth century in the Yangzi Valley. [ 25 ] A bronze tomahawk with a blade of meteoric iron excavated near the city of Gaocheng in Shijiazhuang ( now Hebei province ) has been dated to the fourteenth century BC. An Iron Age culture of the Tibetan Plateau has tentatively been associated with the Zhang Zhung polish described in early Tibetan writings .
ancient China
chinese historians in late periods were accustomed to the notion of one dynasty succeeding another, but the political site in early China was a lot more complicate. Hence, as some scholars of China suggest, the Xia and the Shang can refer to political entities that existed concurrently, just as the early Zhou existed at the same time as the Shang. [ 26 ]
Xia dynasty ( 2070–1600 BC )
The Xia dynasty of China ( from c. 2070 to c. 1600 BC ) is the earliest of the Three Dynasties described in ancient historic records such as Sima Qian ‘s Records of the Grand Historian and Bamboo Annals. The dynasty was considered fabulous by historians until scientific excavations found early Bronze Age sites at Erlitou, Henan in 1959. With few authorize records matching the Shang prophet bones, it remains ill-defined whether these sites are the remains of the Xia dynasty or of another culture from the same period. Excavations that overlap the allege prison term period of the Xia indicate a character of culturally alike groupings of chiefdoms. [ 27 ] Early markings from this time period found on pottery and shells are thought to be ancestral to modern taiwanese characters. [ 28 ] According to ancient records, the dynasty ended around 1600 BC as a consequence of the Battle of Mingtiao .
Shang dynasty ( 1600–1046 BC )
archaeological attest, such as oracle bones and bronzes, and transmitted text attest to the diachronic being of the Shang dynasty ( c. 1600–1046 BC ). Findings from the earlier Shang period comes from excavations at Erligang, near present day Zhengzhou, and Shangcheng. Findings from the former Shang or Yin ( 殷 ) period, were found in profusion at Anyang, in contemporary Henan, the concluding of the Shang ‘s nine capitals ( c. 1300–1046 BC ). [ citation needed ] The findings at Anyang include the earliest written criminal record of the Chinese indeed far discovered : inscriptions of divination records in ancient chinese writing on the bones or shells of animals—the “ oracle bones “, dating from around 1250 BC. [ 1 ]
 Bronze ding ( caldron ) with human faces A series of thirty-one kings reigned over the Shang dynasty. During their reign, according to the Records of the Grand Historian, the capital city was moved six times. [ 30 ] The final ( and most important ) move was to Yin in around 1300 BC which led to the dynasty ‘s golden old age. [ 30 ] The term Yin dynasty has been synonymous with the Shang dynasty in history, although it has recently been used to refer specifically to the latter half of the Shang dynasty. Although written records found at Anyang confirm the universe of the Shang dynasty, [ 31 ] western scholars are frequently hesitant to associate settlements that are contemporaneous with the Anyang village with the Shang dynasty. For exemplar, archaeological findings at Sanxingdui suggest a technologically promote civilization culturally unlike Anyang. The evidence is inconclusive in proving how far the Shang kingdom extended from Anyang. The lead hypothesis is that Anyang, ruled by the same Shang in the official history, coexisted and traded with numerous other culturally divers settlements in the area that is now referred to as China proper. [ 32 ]
Bronze ding ( caldron ) with human faces A series of thirty-one kings reigned over the Shang dynasty. During their reign, according to the Records of the Grand Historian, the capital city was moved six times. [ 30 ] The final ( and most important ) move was to Yin in around 1300 BC which led to the dynasty ‘s golden old age. [ 30 ] The term Yin dynasty has been synonymous with the Shang dynasty in history, although it has recently been used to refer specifically to the latter half of the Shang dynasty. Although written records found at Anyang confirm the universe of the Shang dynasty, [ 31 ] western scholars are frequently hesitant to associate settlements that are contemporaneous with the Anyang village with the Shang dynasty. For exemplar, archaeological findings at Sanxingdui suggest a technologically promote civilization culturally unlike Anyang. The evidence is inconclusive in proving how far the Shang kingdom extended from Anyang. The lead hypothesis is that Anyang, ruled by the same Shang in the official history, coexisted and traded with numerous other culturally divers settlements in the area that is now referred to as China proper. [ 32 ]
Zhou dynasty ( 1046–256 BC )
The Zhou dynasty ( 1046 BC to approximately 256 BC ) is the longest-lasting dynasty in chinese history. By the end of the 2nd millennium BC, the Zhou dynasty began to emerge in the Yellow River valley, overrunning the territory of the Shang. The Zhou appeared to have begun their rule under a semi-feudal system. The Zhou lived west of the Shang, and the Zhou leader was appointed western Protector by the Shang. The ruler of the Zhou, King Wu, with the aid of his brother, the Duke of Zhou, as regent, managed to defeat the Shang at the Battle of Muye. The king of Zhou at this time invoked the concept of the Mandate of Heaven to legitimize his convention, a concept that was influential for about every succeeding dynasty. [ citation needed ] Like Shangdi, Heaven ( tian ) ruled over all the early gods, and it decided who would rule China. [ 33 ] It was believed that a rule lost the Mandate of Heaven when natural disasters occurred in great number, and when, more realistically, the sovereign had apparently lost his concern for the people. In reply, the royal house would be overthrown, and a new house would rule, having been granted the Mandate of Heaven. The Zhou initially moved their capital west to an area near modern Xi’an, on the Wei River, a feeder of the Yellow River, but they would preside over a series of expansions into the Yangtze River valley. This would be the beginning of many population migrations from north to south in chinese history .
spring and Autumn menstruation ( 722–476 BC )
In the eighth century BC, power became decentralized during the give and Autumn period, named after the influential Spring and Autumn Annals. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and compete for hegemony. The position was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples from the northwest, such as the Qin, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. This marks the moment major phase of the Zhou dynasty : the Eastern Zhou. The leap and Autumn period is marked by a falling apart of the central Zhou world power. In each of the hundreds of states that finally arose, local strongmen held most of the political ability and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name alone. Some local leaders even started using royal titles for themselves. China now consisted of hundreds of states, some of them entirely arsenic large as a village with a garrison. As the era continued, larger and more brawny states annexed or claimed suzerainty over smaller ones. By the sixth century BC most humble states had disappeared by being annex and just a few large and brawny principalities dominated China. Some southern states, such as Chu and Wu, claimed independence from the Zhou, who undertook wars against some of them ( Wu and Yue ). many new cities were established in this menstruation and chinese culture was slowly shaped. once all these potent rulers had firm established themselves within their respective dominions, the bloodshed focused more amply on interstate dispute in the Warring States time period, which began when the three remaining élite families in the Jin state—Zhao, Wei and Han—partitioned the submit. many celebrated individuals such as Laozi, Confucius and Sun Tzu lived during this chaotic time period. The Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential cerebral movements as Confucianism, Taoism, Legalism and Mohism were founded, partially in reply to the changing political universe. The first two philosophic thoughts would have an enormous influence on chinese culture .
Warring States period ( 476–221 BC )
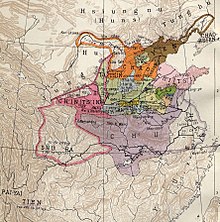 The Warring States. Qin is shown in pink After foster political consolidation, seven big states remained by the end of the fifth hundred BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other are known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a front man and held little real number office. numerous developments were made during this period in culture and mathematics. Examples include an important literary accomplishment, the Zuo zhuan on the Spring and Autumn Annals, which summarizes the preceding spring and Autumn period, and the bunch of 21 bamboo slips from the Tsinghua collection, which was invented during this period dated to 305 BC, are the earth ‘s earliest example of a two digit decimal multiplication mesa, indicating that sophisticated commercial arithmetic was already established during this period. [ 34 ] As neighbor territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning, were annexed, they were governed under the new local administrative system of commandership and prefecture. This system had been in consumption since the give and Autumn period, and parts can silent be seen in the modern arrangement of Sheng and Xian ( state and county ). The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His union of the early six powers, and promote annexations in the modern regions of Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong and Guangxi in 214 BC, enabled him to proclaim himself the First Emperor ( Qin Shi Huang ) .
The Warring States. Qin is shown in pink After foster political consolidation, seven big states remained by the end of the fifth hundred BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other are known as the Warring States period. Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a front man and held little real number office. numerous developments were made during this period in culture and mathematics. Examples include an important literary accomplishment, the Zuo zhuan on the Spring and Autumn Annals, which summarizes the preceding spring and Autumn period, and the bunch of 21 bamboo slips from the Tsinghua collection, which was invented during this period dated to 305 BC, are the earth ‘s earliest example of a two digit decimal multiplication mesa, indicating that sophisticated commercial arithmetic was already established during this period. [ 34 ] As neighbor territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan and Liaoning, were annexed, they were governed under the new local administrative system of commandership and prefecture. This system had been in consumption since the give and Autumn period, and parts can silent be seen in the modern arrangement of Sheng and Xian ( state and county ). The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng, the king of Qin. His union of the early six powers, and promote annexations in the modern regions of Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong and Guangxi in 214 BC, enabled him to proclaim himself the First Emperor ( Qin Shi Huang ) .
imperial China
“ empire of China ” and “ chinese conglomerate ” redirect here. For the empire founded by Yuan Shikai, see Empire of China ( 1915–1916 ) The Imperial China Period can be divided into three sub-periods : early, Middle, and Late. [ citation needed ] major events in the early sub-period include the Qin fusion of China and their successor by the Han, the First Split followed by the Jin fusion, and the loss of north China. The Middle sub-period was marked by the Sui union and their supplement by the Tang, the Second Split, and the Song fusion. The former sub-period included the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties .
Qin dynasty ( 221–206 BC )
Historians frequently refer to the period from the Qin dynasty to the end of the Qing dynasty as Imperial China. [ citation needed ] Though the incorporate reign of the First Qin Emperor lasted only 12 years, he managed to subdue bang-up parts of what constitutes the kernel of the Han Chinese fatherland and to unite them under a tightly centralized Legalist politics seated at Xianyang ( close to modern Xi’an ). The doctrine of Legalism that guided the Qin emphasized rigorous attachment to a legal code and the absolute power of the emperor butterfly. This philosophy, while effective for expanding the conglomerate in a military fashion, proved impracticable for governing it in peacetime. The Qin Emperor presided over the brutal silence of political resistance, including the event known as the burn of books and immerse of scholars. This would be the impulse behind the later Han synthesis incorporating the more mince schools of political government .
major contributions of the Qin include the concept of a centralized government, and the fusion and growth of the legal code, the written language, measurement, and currency of China after the tribulations of the bounce and Autumn and Warring States periods. even something equally basic as the length of axles for carts—which need to match ruts in the roads—had to be made uniform to ensure a feasible trade system throughout the empire. besides as separate of its centralization, the Qin connected the northerly border walls of the states it defeated, making the first base, though rough in, adaptation of the Great Wall of China. The tribe of the north, jointly called the Wu Hu by the Qin, were free from chinese rule during the majority of the dynasty. [ 35 ] Prohibited from trade with Qin dynasty peasants, the Xiongnu kin survive in the Ordos region in northwest China much raided them rather, prompting the Qin to retaliate. After a military campaign led by General Meng Tian, the region was conquered in 215 BC and agribusiness was established ; the peasants, however, were discontented and late revolted. The succeeding Han dynasty besides expanded into the Ordos due to overpopulation, but depleted their resources in the process. indeed, this was true of the dynasty ‘s borders in multiple directions ; modern Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, Tibet, Manchuria, and regions to the southeast were extraneous to the Qin, and even areas over which they had military control were culturally distinct. [ 36 ] After Qin Shi Huang ‘s sudden death, probably due to the consumption of mercury pills, [ 37 ] the Qin politics drastically deteriorated and finally capitulated in 207 BC after the Qin capital was captured and sacked by rebels, which would ultimately lead to the administration of a newfangled dynasty of a coordinated China. [ 38 ] Despite the short 15-year duration of the Qin dynasty, it was vastly influential on China and the social organization of future taiwanese dynasties .
Han dynasty ( 206 BC – AD 220 )
westerly Han
 Map showing the expansion of Han dynasty in the second century BC The Han dynasty was founded by Liu Bang, who emerged triumphant in the Chu–Han Contention that followed the fall of the Qin dynasty. A gold historic period in taiwanese history, the Han dynasty ‘s long period of stability and prosperity consolidated the foundation of China as a coordinated express under a cardinal imperial bureaucracy, which was to end intermittently for most of the adjacent two millennium. During the Han dynasty, territory of China was extended to most of the China proper and to areas far west. confucianism was formally elevated to orthodox status and was to shape the subsequent taiwanese culture. Art, polish and skill all advanced to unprecedented heights. With the heavy and durable impacts of this period of taiwanese history, the dynasty diagnose “ Han ” had been taken as the identify of the chinese people, now the dominant heathen group in modern China, and had been normally used to refer to chinese terminology and written characters. After the initial individualistic policies of Emperors Wen and Jing, the ambitious Emperor Wu brought the conglomerate to its zenith. To consolidate his baron, he extended condescension to Confucianism, which emphasizes constancy and orderliness in a well-structured company. imperial Universities were established to support its study. At the urge of his Legalist advisors, however, he besides strengthened the fiscal structure of the dynasty with government monopolies .
Map showing the expansion of Han dynasty in the second century BC The Han dynasty was founded by Liu Bang, who emerged triumphant in the Chu–Han Contention that followed the fall of the Qin dynasty. A gold historic period in taiwanese history, the Han dynasty ‘s long period of stability and prosperity consolidated the foundation of China as a coordinated express under a cardinal imperial bureaucracy, which was to end intermittently for most of the adjacent two millennium. During the Han dynasty, territory of China was extended to most of the China proper and to areas far west. confucianism was formally elevated to orthodox status and was to shape the subsequent taiwanese culture. Art, polish and skill all advanced to unprecedented heights. With the heavy and durable impacts of this period of taiwanese history, the dynasty diagnose “ Han ” had been taken as the identify of the chinese people, now the dominant heathen group in modern China, and had been normally used to refer to chinese terminology and written characters. After the initial individualistic policies of Emperors Wen and Jing, the ambitious Emperor Wu brought the conglomerate to its zenith. To consolidate his baron, he extended condescension to Confucianism, which emphasizes constancy and orderliness in a well-structured company. imperial Universities were established to support its study. At the urge of his Legalist advisors, however, he besides strengthened the fiscal structure of the dynasty with government monopolies .
 Left image: Western-Han painted ceramic jar decorated with raised taotie
Left image: Western-Han painted ceramic jar decorated with raised taotie
Right image: Reverse side of a Western-Han : Western-Han painted ceramic jolt decorated with raised reliefs of dragons phoenixes, and : change by reversal side of a Western-Han bronze mirror with motley designs of a flower theme major military campaigns were launched to weaken the mobile Xiongnu Empire, limiting their influence north of the Great Wall. Along with the diplomatic efforts led by Zhang Qian, the sphere of influence of the Han Empire extended to the states in the Tarim Basin, opened up the Silk Road that connected China to the west, stimulating bilateral barter and cultural exchange. To the south, versatile small kingdoms far beyond the Yangtze River Valley were formally incorporated into the empire .

 A chinese crossbow mechanism with a buttplate from either the late Warring States Period or the early Han dynasty ; made of tan and inlaid with silver Emperor Wu besides dispatched a series of military campaigns against the Baiyue tribe. The Han annexed Minyue in 135 BC and 111 BC, Nanyue in 111 BC, and Dian in 109 BC. [ 39 ] Migration and military expeditions led to the cultural acculturation of the south. [ 40 ] It besides brought the Han into contact with kingdoms in Southeast Asia, introducing diplomacy and craft. [ 41 ] After Emperor Wu, the empire slipped into gradual stagnation and descent. economically, the state treasury was strained by excessive campaigns and projects, while nation acquisitions by elite families gradually drained the tax base. assorted run clans exerted increasing master over strings of bungling emperors and finally the dynasty was briefly interrupted by the usurpation of Wang Mang .
A chinese crossbow mechanism with a buttplate from either the late Warring States Period or the early Han dynasty ; made of tan and inlaid with silver Emperor Wu besides dispatched a series of military campaigns against the Baiyue tribe. The Han annexed Minyue in 135 BC and 111 BC, Nanyue in 111 BC, and Dian in 109 BC. [ 39 ] Migration and military expeditions led to the cultural acculturation of the south. [ 40 ] It besides brought the Han into contact with kingdoms in Southeast Asia, introducing diplomacy and craft. [ 41 ] After Emperor Wu, the empire slipped into gradual stagnation and descent. economically, the state treasury was strained by excessive campaigns and projects, while nation acquisitions by elite families gradually drained the tax base. assorted run clans exerted increasing master over strings of bungling emperors and finally the dynasty was briefly interrupted by the usurpation of Wang Mang .
Xin dynasty
In AD 9, the usurper Wang Mang claimed that the Mandate of Heaven called for the end of the Han dynasty and the rise of his own, and he founded the ephemeral Xin dynasty. Wang Mang started an extensive broadcast of land and other economic reforms, including the outlaw of slavery and land nationalization and redistribution. These programs, however, were never supported by the landholding families, because they favored the peasants. The instability of world power brought about chaos, uprisings, and loss of territories. This was compounded by mass deluge of the Yellow River ; silt buildup caused it to split into two channels and displaced large numbers of farmers. Wang Mang was finally killed in Weiyang Palace by an enrage peasant syndicate in AD 23 .
Eastern Han
Emperor Guangwu reinstated the Han dynasty with the support of landholding and merchant families at Luoyang, east of the former capital Xi’an. therefore, this new era is termed the Eastern Han dynasty. With the capable administrations of Emperors Ming and Zhang, former glories of the dynasty was reclaimed, with brilliant military and cultural achievements. The Xiongnu Empire was decisively defeated. The diplomat and general Ban Chao further expanded the conquests across the Pamirs to the shores of the Caspian Sea, [ 42 ] therefore reopening the Silk Road, and bringing barter, alien cultures, along with the arrival of Buddhism. With across-the-board connections with the west, the first of several Roman embassies to China were recorded in chinese sources, coming from the sea route in AD 166, and a second one in AD 284. The Eastern Han dynasty was one of the most prolific era of skill and engineering in ancient China, notably the historic invention of papermaking by Cai Lun, and the numerous scientific and mathematical contributions by the celebrated polymath Zhang Heng .
Three Kingdoms ( AD 220–280 )
 Three Kingdoms in 262, on the eve of the seduction of Shu, Wei, and Wu By the second hundred, the empire declined amidst land acquisitions, invasions, and feuding between consort clans and eunuch. The yellow Turban Rebellion broke out in AD 184, ushering in an era of warlords. In the ensuing tumult, three states tried to gain predomination in the period of the Three Kingdoms, since greatly romanticized in works such as Romance of the Three Kingdoms. After Cao Cao reunified the north in 208, his son proclaimed the Wei dynasty in 220. soon, Wei ‘s rivals Shu and Wu proclaimed their independence, leading China into the Three Kingdoms period. This period was characterized by a gradual decentralization of the state that had existed during the Qin and Han dynasties, and an increase in the might of great families. In 266, the Jin dynasty overthrew the Wei and belated unified the area in 280, but this marriage was ephemeral .
Three Kingdoms in 262, on the eve of the seduction of Shu, Wei, and Wu By the second hundred, the empire declined amidst land acquisitions, invasions, and feuding between consort clans and eunuch. The yellow Turban Rebellion broke out in AD 184, ushering in an era of warlords. In the ensuing tumult, three states tried to gain predomination in the period of the Three Kingdoms, since greatly romanticized in works such as Romance of the Three Kingdoms. After Cao Cao reunified the north in 208, his son proclaimed the Wei dynasty in 220. soon, Wei ‘s rivals Shu and Wu proclaimed their independence, leading China into the Three Kingdoms period. This period was characterized by a gradual decentralization of the state that had existed during the Qin and Han dynasties, and an increase in the might of great families. In 266, the Jin dynasty overthrew the Wei and belated unified the area in 280, but this marriage was ephemeral .
Jin dynasty ( AD 266–420 )
Jin dynasty ( AD 266–420 ) Western Jin Dynasty, c. 280 AD
Western Jin Dynasty, c. 280 AD

 “ The Painting of Goddess Luo Rhapsody ” ( in a separate ), Gu Kaizhi, Jin Dynasty The Jin dynasty was sternly weakened by internecine fight among imperial princes and lost command of northern China after non-Han chinese settlers rebelled and captured Luoyang and Chang’an. In 317, a Jin prince in contemporary Nanjing became emperor and continued the dynasty, now known as the Eastern Jin, which held southerly China for another hundred. Prior to this affect, historians refer to the Jin dynasty as the western Jin. Northern China fragmented into a series of autonomous kingdoms, most of which were founded by Xiongnu, Xianbei, Jie, Di and Qiang rulers. These non-Han peoples were ancestors of the Turks, Mongols, and Tibetans. Many had, to some extent, been “ sinicized “ long before their rise to power. In fact, some of them, notably the Qiang and the Xiongnu, had already been allowed to live in the frontier regions within the Great Wall since late Han times. During the period of the Sixteen Kingdoms, war ravaged the north and prompted large-scale Han Chinese migration south to the Yangtze River Basin and Delta .
“ The Painting of Goddess Luo Rhapsody ” ( in a separate ), Gu Kaizhi, Jin Dynasty The Jin dynasty was sternly weakened by internecine fight among imperial princes and lost command of northern China after non-Han chinese settlers rebelled and captured Luoyang and Chang’an. In 317, a Jin prince in contemporary Nanjing became emperor and continued the dynasty, now known as the Eastern Jin, which held southerly China for another hundred. Prior to this affect, historians refer to the Jin dynasty as the western Jin. Northern China fragmented into a series of autonomous kingdoms, most of which were founded by Xiongnu, Xianbei, Jie, Di and Qiang rulers. These non-Han peoples were ancestors of the Turks, Mongols, and Tibetans. Many had, to some extent, been “ sinicized “ long before their rise to power. In fact, some of them, notably the Qiang and the Xiongnu, had already been allowed to live in the frontier regions within the Great Wall since late Han times. During the period of the Sixteen Kingdoms, war ravaged the north and prompted large-scale Han Chinese migration south to the Yangtze River Basin and Delta .
Northern and Southern dynasties ( AD 420–589 )
In the early fifth century, China entered a period known as the Northern and Southern dynasties, in which twin regimes ruled the northern and southerly halves of the area. In the south, the Eastern Jin gave means to the Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang and finally Chen. Each of these southern dynasties were led by Han Chinese ruling families and used Jiankang ( modern Nanjing ) as the das kapital. They held off attacks from the north and preserved many aspects of chinese civilization, while northerly peasant regimes began to sinify. In the north, the final of the Sixteen Kingdoms was extinguished in 439 by the Northern Wei, a kingdom founded by the Xianbei, a mobile people who unified northerly China. The Northern Wei finally split into the Eastern and Western Wei, which then became the Northern Qi and Northern Zhou. These regimes were dominated by Xianbei or Han Chinese who had married into Xianbei families. During this period most Xianbei people adopted Han surnames, finally leading to complete assimilation into the Han. Despite the division of the country, Buddhism spread throughout the land. In southerly China, fierce debates about whether Buddhism should be allowed were held frequently by the royal court and nobles. By the conclusion of the era, Buddhists and Taoists had become much more kind of each other .
Sui dynasty ( AD 581–618 )
Sui dynasty ( AD 581–618 ) Sui dynasty c. 609
Sui dynasty c. 609 Yang Guang depicted as Emperor Yang of Sui The ephemeral Sui dynasty was a pivotal period in chinese history. Founded by Emperor Wen in 581 in succession of the Northern Zhou, the Sui went on to conquer the Southern Chen in 589 to reunify China, ending three centuries of political division. The Sui pioneered many newly institutions, including the government organization of Three Departments and Six Ministries, imperial examinations for selecting officials from commoners, while improved on the systems of fubing arrangement of the united states army conscription and the Equal-field system of land distributions. These policies, which were adopted by later dynasties, brought enormous population growth, and amassed excessive wealth to the state. standardized neologism were enforced throughout the coordinated empire. Buddhism took root as a big religion and was supported officially. Sui China was known for its numerous mega-construction projects. Intended for grains cargo and transporting troops, the Grand Canal was constructed, linking the capitals Daxing ( Chang’an ) and Luoyang to the affluent southeasterly area, and in another route, to the northeast border. The Great Wall was besides expanded, while series of military conquests and diplomatic maneuvers further pacified its borders. however, the massive invasions of the korean Peninsula during the Goguryeo–Sui War failed disastrously, triggering widespread revolts that led to the hang of the dynasty .
Yang Guang depicted as Emperor Yang of Sui The ephemeral Sui dynasty was a pivotal period in chinese history. Founded by Emperor Wen in 581 in succession of the Northern Zhou, the Sui went on to conquer the Southern Chen in 589 to reunify China, ending three centuries of political division. The Sui pioneered many newly institutions, including the government organization of Three Departments and Six Ministries, imperial examinations for selecting officials from commoners, while improved on the systems of fubing arrangement of the united states army conscription and the Equal-field system of land distributions. These policies, which were adopted by later dynasties, brought enormous population growth, and amassed excessive wealth to the state. standardized neologism were enforced throughout the coordinated empire. Buddhism took root as a big religion and was supported officially. Sui China was known for its numerous mega-construction projects. Intended for grains cargo and transporting troops, the Grand Canal was constructed, linking the capitals Daxing ( Chang’an ) and Luoyang to the affluent southeasterly area, and in another route, to the northeast border. The Great Wall was besides expanded, while series of military conquests and diplomatic maneuvers further pacified its borders. however, the massive invasions of the korean Peninsula during the Goguryeo–Sui War failed disastrously, triggering widespread revolts that led to the hang of the dynasty .
Tang dynasty ( AD 618–907 )
The Tang dynasty was a golden age of chinese civilization, a golden, stable, and creative period with meaning developments in culture, artwork, literature, peculiarly poetry, and engineering. Buddhism became the prevailing religion for the coarse people. Chang’an ( modern Xi’an ), the home capital, was the largest city in the earth during its time. [ 43 ] The foremost emperor butterfly, Emperor Gaozu, came to the enthrone on 18 June 618, placed there by his son, Li Shimin, who became the moment emperor butterfly, Taizong, one of the greatest emperors in chinese history. Combined military conquests and diplomatic maneuvers reduced threats from central asian tribe, extended the bound, and brought neighboring states into a feeder organization. military victories in the Tarim Basin kept the Silk Road assailable, connecting Chang’an to Central Asia and areas far to the west. In the south, lucrative nautical trade routes from larboard cities such as Guangzhou connected with aloof countries, and foreign merchants settled in China, encouraging a cosmopolitan culture. The Tang culture and sociable systems were observed and adapted by neighboring countries, most notably Japan. internally the Grand Canal linked the political heartland in Chang’an to the agrarian and economic centers in the eastern and southerly parts of the empire. Xuanzang, a chinese Buddhist monk, learner, traveler, and translator who travelled to India on his own, and returned with, “ over six hundred Mahayana and Hinayana textbook, seven statues of the Buddha and more than a hundred sarira relics. ” The prosperity of the early Tang dynasty was abetted by a centralized bureaucracy. The government was organized as “ Three Departments and Six Ministries “ to individually draft, review, and enforce policies. These departments were run by imperial family members and down aristocrats, but as the dynasty wear on, were joined or replaced by scholar officials selected by imperial examinations, setting patterns for subsequently dynasties. Under the Tang “ equal-field system “ all kingdom was owned by the Emperor and granted to each family according to family size. man granted farming were conscripted for military service for a fixed period each year, a military policy known as the “ Fubing organization “. These policies stimulated a rapid growth in productiveness and a significant united states army without much burden on the state department of the treasury. By the dynasty ‘s center, however, standing armies had replaced conscription, and nation was continuously falling into the hands of secret owners and religious institutions granted exemptions .
 A gilt Buddhist reliquary with decorations of armor guards, from Silla, 7th-century
A gilt Buddhist reliquary with decorations of armor guards, from Silla, 7th-century A Tang period gilt -silver jolt, shaped in the style of northerly nomad ‘s leather bag decorated with a cavalry dancing with a cup of wine in its mouth, as the horses of Emperor Xuanzong were trained to do. The dynasty continued to flourish under the predominate of Empress Wu Zetian, the lone empress regnant in chinese history, and reached its zenith during the long reign of Emperor Xuanzong, who oversaw an conglomerate that stretched from the Pacific to the Aral Sea with at least 50 million people. There were vibrant artistic and cultural creations, including works of the greatest chinese poets, Li Bai and Du Fu .
A Tang period gilt -silver jolt, shaped in the style of northerly nomad ‘s leather bag decorated with a cavalry dancing with a cup of wine in its mouth, as the horses of Emperor Xuanzong were trained to do. The dynasty continued to flourish under the predominate of Empress Wu Zetian, the lone empress regnant in chinese history, and reached its zenith during the long reign of Emperor Xuanzong, who oversaw an conglomerate that stretched from the Pacific to the Aral Sea with at least 50 million people. There were vibrant artistic and cultural creations, including works of the greatest chinese poets, Li Bai and Du Fu .
At the zenith of prosperity of the empire, the An Lushan rebellion from 755 to 763 was a watershed event. War, disease, and economic break devastated the population and drastically weakened the central imperial politics. Upon suppression of the rebellion, regional military governors, known as Jiedushi, gained increasingly autonomous condition. With loss of gross from domain tax, the central imperial government came to rely heavy on strategic arms limitation talks monopoly. outwardly, former submissive states raided the empire and the huge edge territories were lost for centuries. Nevertheless, civil society recovered and thrived amidst the hurt imperial bureaucracy. In former Tang menstruation, the empire was worn out by recurring revolts of regional warlords, while internally, as scholar-officials engaged in cutthroat factional strife, corrupted eunuch amassed huge office. catastrophically, the Huang Chao Rebellion, from 874 to 884, devastated the integral empire for a ten. The sack of the southerly larboard Guangzhou in 879 was followed by the slaughter of most of its inhabitants, specially the large foreign merchant enclaves. [ 45 ] [ 46 ] By 881, both capitals, Luoyang and Chang’an, fell successively. The reliance on cultural Han and Turkic warlords in suppressing the rebellion increased their ability and charm. consequently, the capitulation of the dynasty following Zhu Wen ‘s usurpation led to an era of class .
Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms ( AD 907–960 )
The time period of political disunity between the Tang and the Song, known as the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, lasted from 907 to 960. During this half-century, China was in all respects a multi-state system. Five regimes, namely, ( Later ) Liang, Tang, Jin, Han and Zhou, quickly succeeded one another in master of the traditional Imperial heartland in northerly China. Among the regimes, rulers of ( Later ) Tang, Jin and Han were sinicized Shatuo Turks, which ruled over the heathen majority of Han Chinese. More stable and smaller regimes of by and large ethnic Han rulers coexisted in south and western China over the time period, cumulatively constituted the “ Ten Kingdoms ”. Amidst political chaos in the north, the strategic Sixteen Prefectures ( region along today ‘s Great Wall ) were ceded to the emerging Khitan Liao dynasty, which drastically weakened the defense of the China proper against northern mobile empires. To the south, Vietnam gained lasting independence after being a taiwanese prefecture for many centuries. With wars dominated in Northern China, there were mass south migrations of population, which far enhanced the southbound shift of cultural and economic centers in China. The era ended with the coup d’etat of Later Zhou general Zhao Kuangyin, and the administration of the Song dynasty in 960, which finally annihilated the remains of the “ Ten Kingdoms ” and reunified China .
Read more: A Man Quotes Maritime Law To Avoid Ticket
Song, Liao, Jin, and western Xia dynasties ( AD 960–1279 )
In 960, the Song dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu, with its capital established in Kaifeng ( besides known as Bianjing ). In 979, the Song dynasty reunified most of the China proper, while large swaths of the extinct territories were occupied by sinicized mobile empires. The Khitan Liao dynasty, which lasted from 907 to 1125, ruled over Manchuria, Mongolia, and parts of Northern China. interim, in what are now the north-western chinese provinces of Gansu, Shaanxi, and Ningxia, the Tangut tribe founded the westerly Xia dynasty from 1032 to 1227 .
Aiming to recover the strategic Sixteen Prefectures lost in the former dynasty, campaigns were launched against the Liao dynasty in the early on Song period, which all ended in failure. then in 1004, the Liao cavalry swept over the exposed North China Plain and reached the outskirts of Kaifeng, forcing the Song ‘s submission and then agreement to the Chanyuan Treaty, which imposed heavy annual tributes from the Song department of the treasury. The treaty was a significant reversal of chinese authority of the traditional tributary system. Yet the annual outflow of Song ‘s silver to the Liao was paid back through the purchase of chinese goods and products, which expanded the Song economy, and replenished its treasury. This dampened the incentive for the Song to further campaign against the Liao. interim, this cross-border trade and reach induced farther sinicization within the Liao Empire, at the expense of its military might which was derived from its primitive mobile life style. exchangeable treaties and social-economical consequences occurred in Song ‘s relations with the Jin dynasty. Within the Liao Empire, the Jurchen tribes revolted against their overlords to establish the Jin dynasty in 1115. In 1125, the devastating Jin body armor annihilated the Liao dynasty, while remnants of Liao woo members fled to Central Asia to found the Qara Khitai Empire ( western Liao dynasty ). Jin ‘s invasion of the Song dynasty followed swiftly. In 1127, Kaifeng was sacked, a massive catastrophe known as the Jingkang Incident, ending the Northern Song dynasty. subsequently the stallion north of China was conquered. The outlive members of Song court regrouped in the new capital city of Hangzhou, and initiated the Southern Song dynasty, which ruled territories south of the Huai River. In the ensuing years, the territory and population of China were divided between the Song dynasty, the Jin dynasty and the western Xia dynasty. The era ended with the Mongol seduction, as westerly Xia fell in 1227, the Jin dynasty in 1234, and last the Southern Song dynasty in 1279. Despite its military weakness, the Song dynasty is widely considered to be the eminent point of classical music chinese culture. The Song economy, facilitated by engineering progress, had reached a flush of sophism credibly spiritual world in world history before its time. The population soared to over 100 million and the support standards of common people improved enormously due to improvements in rice cultivation and the across-the-board handiness of char for production. The capital cities of Kaifeng and subsequently Hangzhou were both the most populous cities in the earth for their time, and encouraged vibrant civil societies unmatched by previous chinese dynasties. Although nation deal routes to the far west were blocked by mobile empires, there were extensive maritime trade wind with neighbor states, which facilitated the use of Song coinage as the de facto currency of exchange. Giant wooden vessels equipped with compasses traveled throughout the China Seas and northerly amerind Ocean. The concept of policy was practised by merchants to hedge the risks of such long-haul maritime shipments. With golden economic activities, the historically first use of paper currentness emerged in the western city of Chengdu, as a supplement to the existing bull coins. The Song dynasty was considered to be the gold senesce of great advancements in skill and technology of China, thanks to innovative scholar-officials such as Su Song ( 1020–1101 ) and Shen Kuo ( 1031–1095 ). Inventions such as the hydro-mechanical astronomic clock, the first continuous and endless power-transmitting chain, woodblock print and newspaper money were all invented during the Song dynasty. There was woo intrigue between the political reformers and conservatives, led by the chancellors Wang Anshi and Sima Guang, respectively. By the mid-to-late thirteenth century, the Chinese had adopted the dogma of Neo-Confucian philosophy formulated by Zhu Xi. enormous literary works were compiled during the Song dynasty, such as the historical work, the Zizhi Tongjian ( “ Comprehensive Mirror to Aid in Government ” ). The invention of movable-type printing further facilitated the unfold of cognition. acculturation and the arts flourished, with grandiose artworks such as Along the River During the Qingming Festival and Eighteen Songs of a Nomad Flute, along with great buddhist painters such as the prolific Lin Tinggui .
The Song dynasty was besides a menstruation of major invention in the history of war. Gunpowder, while invented in the Tang dynasty, was first place into consumption in battlefields by the Song army, inspiring a sequence of new firearms and siege engines designs. During the Southern Song dynasty, as its survival hinged decisively on guarding the Yangtze and Huai River against the cavalry forces from the union, the beginning standing united states navy in China was assembled in 1132, with its admiral ‘s headquarters established at Dinghai. Paddle-wheel warships equipped with trebuchets could launch incendiary bombs made of gunpowder and lime, as recorded in Song ‘s victory over the invade Jin forces at the Battle of Tangdao in the East China Sea, and the Battle of Caishi on the Yangtze River in 1161. The advances in civilization during the Song dynasty came to an abrupt end following the devastating Mongol conquest, during which the population sharply dwindled, with a scar contraction in economy. Despite viciously halting Mongol advance for more than three decades, the Southern Song capital Hangzhou fell in 1276, followed by the final annihilation of the Song standing dark blue at the Battle of Yamen in 1279 .
yuan dynasty ( AD 1271–1368 )
 Mongol successor khanates The Yuan dynasty was formally proclaimed in 1271, when the Great Khan of Mongol, Kublai Khan, one of the grandsons of Genghis Khan, assumed the extra title of Emperor of China, and considered his inherit share of the Mongol Empire as a taiwanese dynasty. In the precede decades, the Mongols had conquered the Jin dynasty in Northern China, and the Southern Song dynasty fell in 1279 after a drawn-out and bloody war. The Mongol Yuan dynasty became the inaugural seduction dynasty in taiwanese history to rule the stallion China proper and its population as an cultural minority. The dynasty besides immediately controlled the mongolian heartland and other regions, inheriting the largest share of territory of the divided Mongol Empire, which roughly coincided with the modern area of China and nearby regions in East Asia. Further expansion of the empire was halted after defeats in the invasions of Japan and Vietnam. Following the previous Jin dynasty, the das kapital of Yuan dynasty was established at Khanbaliq ( besides known as Dadu, contemporary Beijing ). The Grand Canal was reconstructed to connect the distant capital city to economic hubs in southern separate of China, setting the precession and foundation where Beijing would largely remain as the capital of the consecutive regimes that unified China mainland. After the peace treaty in 1304 that ended a series of Mongol civil wars, the emperors of the Yuan dynasty were uphold as the nominal Great Khan ( Khagan ) of the greater Mongol Empire over other Mongol Khanates, which however remained de facto autonomous. The earned run average was known as Pax Mongolica, when much of the asian continent was ruled by the Mongols. For the first and only time in history, the silk road was controlled entirely by a individual state, facilitating the flow of people, trade, and cultural exchange. Network of roads and a postal system were established to connect the huge empire. lucrative nautical craft, developed from the previous Song dynasty, continued to flourish, with Quanzhou and Hangzhou emerging as the largest ports in the populace. adventurous travelers from the far west, most notably the Venetian, Marco Polo, would have settled in China for decades. Upon his render, his contingent travel record inspired generations of chivalric Europeans with the splendors of the far East. The yuan dynasty was the first ancient economy, where composition currentness, known at the time as Jiaochao, was used as the overriding medium of switch over. Its unexclusive issue in the late Yuan dynasty inflicted hyperinflation, which finally brought the downfall of the dynasty .
Mongol successor khanates The Yuan dynasty was formally proclaimed in 1271, when the Great Khan of Mongol, Kublai Khan, one of the grandsons of Genghis Khan, assumed the extra title of Emperor of China, and considered his inherit share of the Mongol Empire as a taiwanese dynasty. In the precede decades, the Mongols had conquered the Jin dynasty in Northern China, and the Southern Song dynasty fell in 1279 after a drawn-out and bloody war. The Mongol Yuan dynasty became the inaugural seduction dynasty in taiwanese history to rule the stallion China proper and its population as an cultural minority. The dynasty besides immediately controlled the mongolian heartland and other regions, inheriting the largest share of territory of the divided Mongol Empire, which roughly coincided with the modern area of China and nearby regions in East Asia. Further expansion of the empire was halted after defeats in the invasions of Japan and Vietnam. Following the previous Jin dynasty, the das kapital of Yuan dynasty was established at Khanbaliq ( besides known as Dadu, contemporary Beijing ). The Grand Canal was reconstructed to connect the distant capital city to economic hubs in southern separate of China, setting the precession and foundation where Beijing would largely remain as the capital of the consecutive regimes that unified China mainland. After the peace treaty in 1304 that ended a series of Mongol civil wars, the emperors of the Yuan dynasty were uphold as the nominal Great Khan ( Khagan ) of the greater Mongol Empire over other Mongol Khanates, which however remained de facto autonomous. The earned run average was known as Pax Mongolica, when much of the asian continent was ruled by the Mongols. For the first and only time in history, the silk road was controlled entirely by a individual state, facilitating the flow of people, trade, and cultural exchange. Network of roads and a postal system were established to connect the huge empire. lucrative nautical craft, developed from the previous Song dynasty, continued to flourish, with Quanzhou and Hangzhou emerging as the largest ports in the populace. adventurous travelers from the far west, most notably the Venetian, Marco Polo, would have settled in China for decades. Upon his render, his contingent travel record inspired generations of chivalric Europeans with the splendors of the far East. The yuan dynasty was the first ancient economy, where composition currentness, known at the time as Jiaochao, was used as the overriding medium of switch over. Its unexclusive issue in the late Yuan dynasty inflicted hyperinflation, which finally brought the downfall of the dynasty .
 Dengfeng Observatory, the first in a series of 27 astronomical observatories built in the early Yuan dynasty.
Dengfeng Observatory, the first in a series of 27 astronomical observatories built in the early Yuan dynasty. The Pagoda of Bailin Temple, an octagonal-based brick pagoda built in 1330 during the reign of Emperor Wenzong, ruler of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty ( 1271–1368 ). While the Mongol rulers of the Yuan dynasty adopted well to chinese polish, their sinicization was of lesser extent compared to earlier conquest dynasties in chinese history. For preserving racial superiority as the conqueror and govern class, traditional mobile customs and heritage from the mongol steppe were held in eminent attentiveness. On the other hand, the Mongol rulers besides adopted flexibly to a diverseness of cultures from many advanced civilizations within the huge empire. traditional social structure and polish in China undergo huge transform during the Mongol dominance. Large group of alien migrants settled in China, who enjoyed elevated social condition over the majority Han Chinese, while enriching chinese acculturation with foreign elements. The class of scholar officials and intellectuals, traditional bearers of elect taiwanese acculturation, lost substantial social status. This stimulated the exploitation of culture of the common folks. There were prolific works in zaju diverseness shows and literary songs ( sanqu ), which were written in a classifiable poetry style known as qu. Novels of common manner gained unprecedented condition and popularity .
The Pagoda of Bailin Temple, an octagonal-based brick pagoda built in 1330 during the reign of Emperor Wenzong, ruler of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty ( 1271–1368 ). While the Mongol rulers of the Yuan dynasty adopted well to chinese polish, their sinicization was of lesser extent compared to earlier conquest dynasties in chinese history. For preserving racial superiority as the conqueror and govern class, traditional mobile customs and heritage from the mongol steppe were held in eminent attentiveness. On the other hand, the Mongol rulers besides adopted flexibly to a diverseness of cultures from many advanced civilizations within the huge empire. traditional social structure and polish in China undergo huge transform during the Mongol dominance. Large group of alien migrants settled in China, who enjoyed elevated social condition over the majority Han Chinese, while enriching chinese acculturation with foreign elements. The class of scholar officials and intellectuals, traditional bearers of elect taiwanese acculturation, lost substantial social status. This stimulated the exploitation of culture of the common folks. There were prolific works in zaju diverseness shows and literary songs ( sanqu ), which were written in a classifiable poetry style known as qu. Novels of common manner gained unprecedented condition and popularity .
 The Ayuwang Stupa in northerly Shanxi, China .
The Ayuwang Stupa in northerly Shanxi, China .
Ming dynasty ( AD 1368–1644 )
The Ming dynasty was founded by Zhu Yuanzhang in 1368, who proclaimed himself as the Hongwu Emperor. The das kapital was initially set at Nanjing, and was late moved to Beijing from Yongle Emperor ‘s reign forth. urbanization increased as the population grew and as the division of labor movement grew more building complex. large urban centers, such as Nanjing and Beijing, besides contributed to the growth of secret industry. In detail, minor industries grew up, often specializing in paper, silk, cotton, and porcelain goods. For the most partially, however, relatively minor urban centers with markets proliferated around the state. Town markets chiefly traded food, with some necessary manufactures such as pins or oil. Despite the xenophobia and cerebral introspection characteristic of the increasingly popular modern school of neo-Confucianism, China under the early Ming dynasty was not detached. Foreign trade and other contacts with the outdoor earth, peculiarly Japan, increased well. chinese merchants explored all of the indian Ocean, reaching East Africa with the voyages of Zheng He. The Hongwu Emperor, being the only founder of a chinese dynasty who was besides of peasant origin, had laid the initiation of a state that relied basically in department of agriculture. Commerce and trade, which flourished in the former Song and Yuan dynasties, were less stress. Neo-feudal landholdings of the Song and Mongol periods were expropriated by the Ming rulers. Land estates were confiscated by the politics, fragmented, and rented out. individual slavery was prevent. consequently, after the death of the Yongle Emperor, autonomous peasant landholders predominated in taiwanese farming. These laws might have paved the way to removing the worst of the poverty during the former regimes. Towards later earned run average of the Ming dynasty, with declining government restraint, commerce, trade wind and private industries revived. The dynasty had a impregnable and complex cardinal government that unified and controlled the empire. The emperor ‘s character became more autocratic, although Hongwu Emperor necessarily continued to use what he called the “ Grand Secretariat “ to assist with the huge paperwork of the bureaucracy, including memorials ( petitions and recommendations to the throne ), imperial edicts in answer, reports of versatile kinds, and tax records. It was this like bureaucracy that by and by prevented the ming politics from being able to adapt to changes in company, and finally led to its decline. The Yongle Emperor strenuously tried to extend China ‘s influence beyond its borders by demanding other rulers send ambassadors to China to present tribute. A boastfully dark blue was built, including four-masted ships displacing 1,500 tons. A standing army of 1 million troops was created. The chinese armies conquered and occupied Vietnam for around 20 years, while the chinese fleet sailed the China seas and the indian Ocean, cruising adenine far as the east coast of Africa. The Chinese gained charm in easterly Moghulistan. several nautical asian nations sent envoys with protection for the chinese emperor. Domestically, the Grand Canal was expanded and became a stimulation to domestic trade. Over 100,000 tons of iron per year were produced. many books were printed using movable type. The imperial palace in Beijing ‘s Forbidden City reached its current magnificence. It was besides during these centuries that the potential of south China came to be fully exploited. New crops were widely cultivated and industries such as those producing porcelain and textiles flourished. In 1449 Esen Tayisi led an Oirat Mongol invasion of northern China which culminated in the capture of the Zhengtong Emperor at Tumu. Since then, the Ming became on the defensive on the northern frontier, which led to the Ming Great Wall being built. Most of what remains of the Great Wall of China today was either built or repaired by the Ming. The brick and granite work was enlarged, the watchtowers were redesigned, and cannons were placed along its distance .
At ocean, the Ming became increasingly isolationist after the death of the Yongle Emperor. The treasure voyages which sailed amerind Ocean were discontinued, and the nautical prohibition laws were set in space banning the Chinese from sailing abroad. european traders who reached China in the midst of the Age of Discovery were repeatedly rebuked in their requests for deal, with the portuguese being repulsed by the Ming dark blue at Tuen Mun in 1521 and again in 1522. domestic and foreign demands for overseas trade, deemed illegal by the state, led to widespread wokou piracy attacking the southeast coastline during the principle of the Jiajing Emperor ( 1507–1567 ), which entirely subsided after the hatchway of ports in Guangdong and Fujian and much military inhibition. [ 49 ] The Portuguese were allowed to settle in Macau in 1557 for trade, which remained in Portuguese hands until 1999. The dutch entry into the chinese sea was besides met with fierce resistor, with the Dutch being chased off the Penghu islands in the Sino-Dutch conflicts of 1622–1624 and were forced to settle in Taiwan rather. The Dutch in Taiwan fight with the Ming in the Battle of Liaoluo Bay in 1633 and lost, and finally surrendered to the Ming loyalist Koxinga in 1662, after the fall of the Ming dynasty. In 1556, during the rule of the Jiajing Emperor, the Shaanxi earthquake killed about 830,000 people, the deadliest earthquake of all prison term. The Ming dynasty intervened profoundly in the japanese invasions of Korea ( 1592–98 ), which ended with the secession of all invading japanese forces in Korea, and the restoration of the Joseon dynasty, its traditional ally and tributary state. The regional hegemony of the Ming dynasty was preserved at a toll on its resources. Coincidentally, with Ming ‘s control in Manchuria in refuse, the Manchu ( Jurchen ) tribe, under their captain Nurhaci, broke away from Ming ‘s rule, and emerged as a potent, mix submit, which was belated proclaimed as the Qing dynasty. It went on to subdue the much weakened Korea as its tributary, conquered Mongolia, and expanded its territory to the outskirt of the Great Wall. The most elite united states army of the Ming dynasty was to station at the Shanhai Pass to guard the survive stronghold against the Manchus, which weakened its suppression of internal peasants uprisings .
Qing dynasty ( AD 1644–1912 )
Qing dynasty ( AD 1644–1912 ) 1836 map of China published by C. Picque .
1836 map of China published by C. Picque . Pilgrim flask, porcelain with underglaze aristocratic and iron-red decoration .
Pilgrim flask, porcelain with underglaze aristocratic and iron-red decoration . A military overdress of the Qianlong Emperor
A military overdress of the Qianlong Emperor
By the end of Qianlong Emperor ‘s long reign in 1796, the Qing Empire was at its zenith. The Qing ruled more than one-third of the universe ‘s population, and had the largest economy in the universe. By area it was one of the largest empires ever .
 Li Hongzhang, a Chinese politician, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. In the nineteenth century the empire was internally restive and outwardly threatened by western powers. The defeat by the british Empire in the First Opium War ( 1840 ) led to the Treaty of Nanking ( 1842 ), under which Hong Kong was ceded to Britain and importing of opium ( produced by british Empire territories ) was allowed. opium custom continued to grow in China, adversely affecting social stability. subsequent military defeats and unequal treaties with other westerly powers continued even after the fall of the Qing dynasty. internally the Taiping Rebellion ( 1851–1864 ), a Christian religious drift led by the “ Heavenly King ” Hong Xiuquan swept from the south to establish the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom and controlled approximately a third of China proper for over a ten. The court in despair empowered Han chinese officials such as Zeng Guofan to raise local armies. After initial defeats, Zeng crushed the rebels in the Third Battle of Nanking in 1864. [ 51 ] This was one of the largest wars in the nineteenth hundred in terms of troop affair ; there was massive passing of life, with a death toll of about 20 million. [ 52 ] A drawstring of civil disturbances followed, including the Punti–Hakka Clan Wars, Nian Rebellion, Dungan Revolt, and Panthay Rebellion. [ 53 ] All rebellions were ultimately put down, but at enormous cost and with millions dead, badly weakening the cardinal imperial authority. China never rebuilt a impregnable cardinal united states army, and many local officials used their military world power to effectively rule independently in their provinces. [ 54 ] Yet the dynasty appeared to recover in the Tongzhi Restoration ( 1860-1872 ), led by Manchu royal family reformers and Han Chinese officials such as Zeng Guofan and his proteges Li Hongzhang and Zuo Zongtang. Their Self-Strengthening Movement made effective institutional reforms, imported western factories and communications technology, with prime stress on strengthening the military. however, the reform was undermined by official rivalries, cynicism, and quarrels within the imperial family. The get the better of of Yuan Shikai ‘s modernized “ Beiyang Fleet “ in the beginning Sino-Japanese War ( 1894–1895 ) led to the constitution of the New Army. The Guangxu Emperor, advised by Kang Youwei, then launched a comprehensive examination reform feat, the Hundred Days ‘ Reform ( 1898 ). Empress Dowager Cixi, however, feared that abrupt change would lead to bureaucratic opposition and alien interposition and cursorily suppressed it .
Li Hongzhang, a Chinese politician, general and diplomat of the late Qing dynasty. In the nineteenth century the empire was internally restive and outwardly threatened by western powers. The defeat by the british Empire in the First Opium War ( 1840 ) led to the Treaty of Nanking ( 1842 ), under which Hong Kong was ceded to Britain and importing of opium ( produced by british Empire territories ) was allowed. opium custom continued to grow in China, adversely affecting social stability. subsequent military defeats and unequal treaties with other westerly powers continued even after the fall of the Qing dynasty. internally the Taiping Rebellion ( 1851–1864 ), a Christian religious drift led by the “ Heavenly King ” Hong Xiuquan swept from the south to establish the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom and controlled approximately a third of China proper for over a ten. The court in despair empowered Han chinese officials such as Zeng Guofan to raise local armies. After initial defeats, Zeng crushed the rebels in the Third Battle of Nanking in 1864. [ 51 ] This was one of the largest wars in the nineteenth hundred in terms of troop affair ; there was massive passing of life, with a death toll of about 20 million. [ 52 ] A drawstring of civil disturbances followed, including the Punti–Hakka Clan Wars, Nian Rebellion, Dungan Revolt, and Panthay Rebellion. [ 53 ] All rebellions were ultimately put down, but at enormous cost and with millions dead, badly weakening the cardinal imperial authority. China never rebuilt a impregnable cardinal united states army, and many local officials used their military world power to effectively rule independently in their provinces. [ 54 ] Yet the dynasty appeared to recover in the Tongzhi Restoration ( 1860-1872 ), led by Manchu royal family reformers and Han Chinese officials such as Zeng Guofan and his proteges Li Hongzhang and Zuo Zongtang. Their Self-Strengthening Movement made effective institutional reforms, imported western factories and communications technology, with prime stress on strengthening the military. however, the reform was undermined by official rivalries, cynicism, and quarrels within the imperial family. The get the better of of Yuan Shikai ‘s modernized “ Beiyang Fleet “ in the beginning Sino-Japanese War ( 1894–1895 ) led to the constitution of the New Army. The Guangxu Emperor, advised by Kang Youwei, then launched a comprehensive examination reform feat, the Hundred Days ‘ Reform ( 1898 ). Empress Dowager Cixi, however, feared that abrupt change would lead to bureaucratic opposition and alien interposition and cursorily suppressed it .
 The national ease up of the Great Qing from 1862 to 1889. ( trilateral adaptation )
The national ease up of the Great Qing from 1862 to 1889. ( trilateral adaptation ) The national masthead of the Great Qing from 1889 to 1912. In the summer of 1900, the Boxer Uprising opposed foreign influence and murdered chinese Christians and extraneous missionaries. When Boxers entered Beijing, the qing government ordered all foreigners to leave, but they and many chinese Christians were besieged in the foreign legations quarter. An Eight-Nation Alliance sent the Seymour Expedition of Japanese, Russian, British, Italian, German, French, American, and austrian troops to relieve the siege, but they were forced to retreat by Boxer and Qing troops at the Battle of Langfang. After the Alliance ‘s attack on the Dagu Forts, the court declared war on the Alliance and authorized the Boxers to join with imperial armies. After boisterous fight at Tientsin, the Alliance formed the moment, much larger Gaselee Expedition and finally reached Beijing ; the Empress Dowager evacuated to Xi’an. The Boxer Protocol ended the war, exacting a enormous damages. The Qing court then instituted “ New Policies “ of administrative and legal reform, including abolition of the examination system. But young officials, military officers, and students debated reform, possibly a constitutional monarchy, or the overrule of the dynasty and the creation of a democracy. They were inspired by an emerging public opinion formed by intellectuals such as Liang Qichao and the revolutionary ideas of Sun Yat-sen. A place military uprise, the Wuchang Uprising, began on 10 October 1911, in Wuchang ( Today region of Wuhan ), and soon spread. The Republic of China was proclaimed on 1 January 1912, ending 2,000 years of dynastic rule .
The national masthead of the Great Qing from 1889 to 1912. In the summer of 1900, the Boxer Uprising opposed foreign influence and murdered chinese Christians and extraneous missionaries. When Boxers entered Beijing, the qing government ordered all foreigners to leave, but they and many chinese Christians were besieged in the foreign legations quarter. An Eight-Nation Alliance sent the Seymour Expedition of Japanese, Russian, British, Italian, German, French, American, and austrian troops to relieve the siege, but they were forced to retreat by Boxer and Qing troops at the Battle of Langfang. After the Alliance ‘s attack on the Dagu Forts, the court declared war on the Alliance and authorized the Boxers to join with imperial armies. After boisterous fight at Tientsin, the Alliance formed the moment, much larger Gaselee Expedition and finally reached Beijing ; the Empress Dowager evacuated to Xi’an. The Boxer Protocol ended the war, exacting a enormous damages. The Qing court then instituted “ New Policies “ of administrative and legal reform, including abolition of the examination system. But young officials, military officers, and students debated reform, possibly a constitutional monarchy, or the overrule of the dynasty and the creation of a democracy. They were inspired by an emerging public opinion formed by intellectuals such as Liang Qichao and the revolutionary ideas of Sun Yat-sen. A place military uprise, the Wuchang Uprising, began on 10 October 1911, in Wuchang ( Today region of Wuhan ), and soon spread. The Republic of China was proclaimed on 1 January 1912, ending 2,000 years of dynastic rule .
modern China
Republic of China ( since 1912 )
The probationary government of the Republic of China was formed in Nanking on 12 March 1912. Sun Yat-sen became President of the Republic of China, but he turned power over to Yuan Shikai, who commanded the New Army. Over the future few years, yuan proceeded to abolish the national and provincial assemblies and declared himself as the emperor of Empire of China in late 1915. Yuan ‘s imperial ambitions were fiercely opposed by his subordinates ; faced with the prospect of rebellion, he abdicated in March 1916 and died of natural causes in June .
yuan ‘s death in 1916 left a might void ; the republican government was all but shattered. This opened the means for the Warlord Era, during which much of China was ruled by shifting coalitions of competing provincial military leaders and the Beiyang government. Intellectuals, disappointed in the failure of the Republic, launched the New Culture Movement .
In 1919, the May Fourth Movement began as a reaction to the pro-Japanese terms imposed on China by the Treaty of Versailles following World War I. It quickly became a countrywide protest movement. The protests were a moral success as the cabinet fell and China refused to sign the Treaty of Versailles, which had awarded german holdings of Shandong to Japan. memory of the mistreatment at Versailles fuels resentment into the twenty-first hundred. [ 55 ] political and cerebral zymosis waxed potent throughout the 1920s and 1930s. According to Patricia Ebrey :
- “Nationalism, patriotism, progress, science, democracy, and freedom were the goals; imperialism, feudalism, warlordism, autocracy, patriarchy, and blind adherence to tradition were the enemies. Intellectuals struggled with how to be strong and modern and yet Chinese, how to preserve China as a political entity in the world of competing nations.”[56]
 The flag of the Republic of China from 1912 to 1928 .
The flag of the Republic of China from 1912 to 1928 . The iris of the Republic of China from 1928 to now. In the 1920s, Sun Yat-sen established a revolutionary base in Guangzhou and set out to unite the break up nation. He welcomed aid from the Soviet Union ( itself fresh from Lenin ‘s Communist coup d’etat ) and he entered into an alliance with the fledgling Chinese Communist Party ( CCP ). After Sun ‘s death from cancer in 1925, one of his protégés, Chiang Kai-shek, seized control of the Nationalist Party ( KMT ) and succeeded in bringing most of south and central China under its rule in the Northern Expedition ( 1926–1927 ). Having defeated the warlords in the confederacy and central China by military force, Chiang was able to secure the noun phrase allegiance of the warlords in the North and establish the patriot government in Nanking. In 1927, Chiang turned on the CCP and relentlessly purged the Communists elements in his NRA. In 1934, driven from their mountain bases such as the Chinese Soviet Republic, the CCP forces embarked on the Long March across China ‘s most bare terrain to the northwesterly, where they established a guerrilla base at Yan’an in Shaanxi Province. During the Long March, the communists reorganized under a new drawing card, Mao Zedong ( Mao Tse-tung ) .
The iris of the Republic of China from 1928 to now. In the 1920s, Sun Yat-sen established a revolutionary base in Guangzhou and set out to unite the break up nation. He welcomed aid from the Soviet Union ( itself fresh from Lenin ‘s Communist coup d’etat ) and he entered into an alliance with the fledgling Chinese Communist Party ( CCP ). After Sun ‘s death from cancer in 1925, one of his protégés, Chiang Kai-shek, seized control of the Nationalist Party ( KMT ) and succeeded in bringing most of south and central China under its rule in the Northern Expedition ( 1926–1927 ). Having defeated the warlords in the confederacy and central China by military force, Chiang was able to secure the noun phrase allegiance of the warlords in the North and establish the patriot government in Nanking. In 1927, Chiang turned on the CCP and relentlessly purged the Communists elements in his NRA. In 1934, driven from their mountain bases such as the Chinese Soviet Republic, the CCP forces embarked on the Long March across China ‘s most bare terrain to the northwesterly, where they established a guerrilla base at Yan’an in Shaanxi Province. During the Long March, the communists reorganized under a new drawing card, Mao Zedong ( Mao Tse-tung ) .
The bitter Chinese Civil War between the Nationalists and the Communists continued, openly or clandestinely, through the 14-year-long japanese occupation of respective parts of the area ( 1931–1945 ). The two chinese parties nominally formed a United Front to oppose the Japanese in 1937, during the second Sino-Japanese War ( 1937–1945 ), which became a function of World War II. japanese forces committed numerous war atrocities against the civilian population, including biological war ( see Unit 731 ) and the Three Alls Policy ( Sankō Sakusen ), the three alls being : “Kill All, Burn All and Loot All”. [ 57 ] Following the get the better of of Japan in 1945, the war between the nationalist government forces and the CCP resumed, after failed attempts at reconciliation and a negotiate colony. By 1949, the CCP had established control over most of the nation. Odd Arne Westad says the Communists won the Civil War because they made fewer military mistakes than Chiang, and because in his search for a brawny centralized government, Chiang antagonized besides many interest groups in China. furthermore, his party was weakened in the war against the Japanese. meanwhile, the Communists told different groups, such as peasants, precisely what they wanted to hear, and cloaked themselves in the shroud of taiwanese Nationalism. [ 58 ] During the civil war both the Nationalists and Communists carried out bulk atrocities, with millions of non-combatants killed by both sides. [ 59 ] These included deaths from forced conscription and massacres. [ 60 ] When the patriot politics forces were defeated by CCP forces in mainland China in 1949, the patriot government retreated to Taiwan with its forces, along with Chiang and a large number of their supporters ; the patriot government had taken effective control of Taiwan at the end of WWII as character of the overall japanese capitulation, when japanese troops in Taiwan surrendered to the Republic of China troops. [ 61 ] Until the early 1970s, the ROC was recognized as the sole legitimate politics of China by the United Nations, the United States and most western nations, refusing to recognize the PRC on report of the Cold War. This changed in 1971 when the PRC was seated in the United Nations, replacing the ROC. The KMT ruled Taiwan under warlike law until 1987, with the submit goal of being argus-eyed against communist infiltration and preparing to retake mainland China. Therefore, political dissent was not tolerated during that period. In the 1990s, the ROC underwent a major democratic reform, beginning with the 1991 resignation of the members of the Legislative Yuan and National Assembly elected in 1947. These groups were originally created to represent mainland China constituencies. besides lifted were the restrictions on the practice of min languages in the air media and in schools. This culminated with the first gear direct presidential election in 1996 against the democratic Progressive Party ( DPP ) campaigner and former dissentient, Peng Min-ming. In 2000, the KMT status as the ruling party ended when the DPP took world power, only to regain its status in the 2008 election by Ma Ying-jeou. due to the controversial nature of the Taiwan ‘s political status, the ROC is presently recognized by 14 UN member states and Holy See as of 2022 as the lawful government of “ China ” .
People ‘s Republic of China ( since 1949 )
major combat in the chinese Civil War ended in 1949 with Kuomintang ( KMT ) pulling out of the mainland, with the government relocating to Taipei and maintaining control only over a few islands. The CCP was left in control of mainland China. On 1 October 1949, Mao Zedong proclaimed the People ‘s Republic of China. [ 62 ] “ communist China ” and “ red China ” were two common names for the PRC. [ 63 ]
 People ‘s Republic of China tenth Anniversary Parade in Beijing The PRC was shaped by a series of campaigns and five-year plans. The economic and sociable plan known as the Great Leap Forward caused an estimated 45 million deaths. [ 64 ] Mao ‘s politics carried out mass executions of landowners, instituted collectivization and implemented the Laogai camp system. performance, deaths from forced british labour party and other atrocities resulted in millions of deaths under Mao. In 1966 Mao and his allies launched the Cultural Revolution, which continued until Mao ‘s death a decade late. The cultural Revolution, motivated by power struggles within the Party and a concern of the Soviet Union, led to a major agitation in chinese society. In 1972, at the acme of the Sino-Soviet separate, Mao and Zhou Enlai met US president Richard Nixon in Beijing to establish relations with the United States. In the same year, the PRC was admitted to the United Nations in place of the Republic of China, with permanent membership of the Security Council .
People ‘s Republic of China tenth Anniversary Parade in Beijing The PRC was shaped by a series of campaigns and five-year plans. The economic and sociable plan known as the Great Leap Forward caused an estimated 45 million deaths. [ 64 ] Mao ‘s politics carried out mass executions of landowners, instituted collectivization and implemented the Laogai camp system. performance, deaths from forced british labour party and other atrocities resulted in millions of deaths under Mao. In 1966 Mao and his allies launched the Cultural Revolution, which continued until Mao ‘s death a decade late. The cultural Revolution, motivated by power struggles within the Party and a concern of the Soviet Union, led to a major agitation in chinese society. In 1972, at the acme of the Sino-Soviet separate, Mao and Zhou Enlai met US president Richard Nixon in Beijing to establish relations with the United States. In the same year, the PRC was admitted to the United Nations in place of the Republic of China, with permanent membership of the Security Council .
 The flag of the People ‘s Republic of China since 1949. A baron clamber followed Mao ‘s death in 1976. The Gang of Four were arrested and blamed for the excesses of the Cultural Revolution, marking the end of a churning political earned run average in China. Deng Xiaoping outmaneuvered Mao ‘s anointed successor chair Hua Guofeng, and gradually emerged as the de facto drawing card over the adjacent few years. Deng Xiaoping was the Paramount Leader of China from 1978 to 1992, although he never became the read/write head of the party or department of state, and his influence within the Party led the country to significant economic reforms. The CCP subsequently loosened governmental control over citizens ‘ personal lives and the communes were disbanded with many peasants receiving multiple land leases, which greatly increased incentives and agrarian production. In addition, there were many free market areas opened. The most successful spare market areas was Shenzhen. It is located in Guangdong and the property tax free area however exists today. This turn of events marked China ‘s transition from a planned economy to a assorted economy with an increasingly open market environment, a organization termed by some [ 65 ] as “ market socialism “, and formally by the CCP as “ Socialism with Chinese characteristics “. The PRC adopted its current united states constitution on 4 December 1982. In 1989 the death of former general secretary Hu Yaobang helped to spark the Tiananmen Square protests of that year, during which students and others campaigned for respective months, speaking out against corruption and in favor of greater political reform, including democratic rights and freedom of language. however, they were finally put down on 4 June when Army troops and vehicles entered and forcibly cleared the square, with considerable numbers of fatalities. This consequence was widely reported, and brought cosmopolitan condemnation and sanctions against the government. [ 66 ] [ 67 ] A filmed incident involving the “ Tank Man “ was seen worldwide. CCP general secretary and PRC President Jiang Zemin and PRC Premier Zhu Rongji, both erstwhile mayors of Shanghai, led post-Tiananmen PRC in the 1990s. Under Jiang and Zhu ‘s ten-spot years of administration, the PRC ‘s economic operation pulled an estimated 150 million peasants out of poverty and sustained an average annual gross domestic product growth rate of 11.2 %. [ 68 ] [ better source needed ] The state formally joined the World Trade Organization in 2001. By 1997 and 1999, former european colonies of british Hong Kong and Portuguese Macau became the Hong Kong and Macau special administrative regions of the People ‘s Republic of China respectively. Although the PRC needs economic growth to spur its development, the government began to worry that rapid economic emergence was degrading the state ‘s resources and environment. Another concern is that certain sectors of club are not sufficiently benefiting from the PRC ‘s economic development ; one example of this is the wide break between urban and rural areas. As a result, under early CCP cosmopolitan secretary and President Hu Jintao and Premier Wen Jiabao, the PRC originate policies to address issues of equitable distribution of resources, but the result was not known as of 2014. [ 69 ] More than 40 million farmers were displaced from their land, [ 70 ] normally for economic development, contributing to 87,000 demonstrations and riots across China in 2005. [ 71 ] For much of the PRC ‘s population, live standards improved very substantially and freedom increased, but political controls remained tight and rural areas hapless. [ 72 ] The outbreak of the novel coronavirus SARS coronavirus 2, which causes COVID-19 disease, in the first place detected in Wuhan became the ball-shaped COVID-19 pandemic. The virus ‘ origin in China has led to misinformation, including conspiracy theories that suggest the virus originated in a chinese lab and was genetically engineered. [ 73 ] [ 74 ] [ 75 ] The World Health Organization concluded that artificial origin of the coronavirus is “ highly improbable ”. [ 76 ] [ 77 ]
The flag of the People ‘s Republic of China since 1949. A baron clamber followed Mao ‘s death in 1976. The Gang of Four were arrested and blamed for the excesses of the Cultural Revolution, marking the end of a churning political earned run average in China. Deng Xiaoping outmaneuvered Mao ‘s anointed successor chair Hua Guofeng, and gradually emerged as the de facto drawing card over the adjacent few years. Deng Xiaoping was the Paramount Leader of China from 1978 to 1992, although he never became the read/write head of the party or department of state, and his influence within the Party led the country to significant economic reforms. The CCP subsequently loosened governmental control over citizens ‘ personal lives and the communes were disbanded with many peasants receiving multiple land leases, which greatly increased incentives and agrarian production. In addition, there were many free market areas opened. The most successful spare market areas was Shenzhen. It is located in Guangdong and the property tax free area however exists today. This turn of events marked China ‘s transition from a planned economy to a assorted economy with an increasingly open market environment, a organization termed by some [ 65 ] as “ market socialism “, and formally by the CCP as “ Socialism with Chinese characteristics “. The PRC adopted its current united states constitution on 4 December 1982. In 1989 the death of former general secretary Hu Yaobang helped to spark the Tiananmen Square protests of that year, during which students and others campaigned for respective months, speaking out against corruption and in favor of greater political reform, including democratic rights and freedom of language. however, they were finally put down on 4 June when Army troops and vehicles entered and forcibly cleared the square, with considerable numbers of fatalities. This consequence was widely reported, and brought cosmopolitan condemnation and sanctions against the government. [ 66 ] [ 67 ] A filmed incident involving the “ Tank Man “ was seen worldwide. CCP general secretary and PRC President Jiang Zemin and PRC Premier Zhu Rongji, both erstwhile mayors of Shanghai, led post-Tiananmen PRC in the 1990s. Under Jiang and Zhu ‘s ten-spot years of administration, the PRC ‘s economic operation pulled an estimated 150 million peasants out of poverty and sustained an average annual gross domestic product growth rate of 11.2 %. [ 68 ] [ better source needed ] The state formally joined the World Trade Organization in 2001. By 1997 and 1999, former european colonies of british Hong Kong and Portuguese Macau became the Hong Kong and Macau special administrative regions of the People ‘s Republic of China respectively. Although the PRC needs economic growth to spur its development, the government began to worry that rapid economic emergence was degrading the state ‘s resources and environment. Another concern is that certain sectors of club are not sufficiently benefiting from the PRC ‘s economic development ; one example of this is the wide break between urban and rural areas. As a result, under early CCP cosmopolitan secretary and President Hu Jintao and Premier Wen Jiabao, the PRC originate policies to address issues of equitable distribution of resources, but the result was not known as of 2014. [ 69 ] More than 40 million farmers were displaced from their land, [ 70 ] normally for economic development, contributing to 87,000 demonstrations and riots across China in 2005. [ 71 ] For much of the PRC ‘s population, live standards improved very substantially and freedom increased, but political controls remained tight and rural areas hapless. [ 72 ] The outbreak of the novel coronavirus SARS coronavirus 2, which causes COVID-19 disease, in the first place detected in Wuhan became the ball-shaped COVID-19 pandemic. The virus ‘ origin in China has led to misinformation, including conspiracy theories that suggest the virus originated in a chinese lab and was genetically engineered. [ 73 ] [ 74 ] [ 75 ] The World Health Organization concluded that artificial origin of the coronavirus is “ highly improbable ”. [ 76 ] [ 77 ]
See besides
References
Citations
Sources
References and farther reading
For a more comprehensive number, see Bibliography of Chinese history
- Berkshire Encyclopedia of China (5 vol. 2009) online
- Clyde, Paul H., and Burton F. Beers. The Far East: A History of Western Impacts and Eastern Responses, 1830-1975 (Prentice Hall, 1975), university textbook. online
- Catchpole, Brian. A map history of modern China (1976), new maps and diagrams
- Cheng, Linsun (2009). Berkshire Encyclopedia of China. Great Barrington, MA: Berkshire Pub. Group. ISBN 978-1933782683.
- Dardess, John W. (2010). Governing China, 150–1850. Hackett Publishing. ISBN 978-1-60384-311-9.
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (2010). The Cambridge Illustrated History of China. Cambridge, England: Cambridge UP. ISBN 978-0521196208.
- Elleman, Bruce A. Modern Chinese Warfare, 1795-1989 (2001) 363 pp.
- Fairbank, John King and Goldman, Merle. China: A New History. 2nd ed. (Harvard UP, 2006). 640 pp.
- Fenby, Jonathan. The Penguin History of Modern China: The Fall and Rise of a Great Power 1850 to the Present (3rd ed. 2019) popular history.
- Gernet, Jacques, J. R. Foster, and Charles Hartman. A History of Chinese Civilization (1996). One-volume survey.
- Hsu, Cho-yun (2012), China: A New Cultural History, Columbia University Press 612 pp. stress on China’s encounters with successive waves of globalization.
- Hsü, Immanuel. The Rise of Modern China, (6th ed. Oxford UP, 1999). Detailed coverage of 1644–1999, in 1136 pp.; stress on diplomacy and politics. online
- Keay, John. China: A History (2009), 642 pp, popular history pre-1760.
- Leung, Edwin Pak-wah. Historical dictionary of revolutionary China, 1839–1976 (1992) online free to borrow
- Leung, Edwin Pak-wah. Political Leaders of Modern China: A Biographical Dictionary (2002)
- Mote, Frederick W. Imperial China, 900–1800 (Harvard UP, 1999), 1,136 pp. Authoritative treatment of the Song, Yuan, Ming, and early Qing dynasties.
- Perkins, Dorothy. Encyclopedia of China: The Essential Reference to China, Its History and Culture. (Facts on File, 1999). 662 pp. online
- Roberts, J. A. G. A Concise History of China. (Harvard U. Press, 1999). 341 pp.
- Stanford, Edward. Atlas of the Chinese Empire, containing separate maps of the eighteen provinces of China (2nd ed 1917) Legible color maps Online free
- Schoppa, R. Keith. The Columbia Guide to Modern Chinese History. (Columbia U. Press, 2000). 356 pp.
- Spence, Jonathan D. The Search for Modern China (1999), 876pp; scholarly survey from 1644 to 1990s online
- Wang, Ke-wen, ed. Modern China: An Encyclopedia of History, Culture, and Nationalism. (1998).online
- Westad, Odd Arne. Restless Empire: China and the World Since 1750 (2012)
- Wright, David Curtis. History of China (2001) 257 pp.
- Wills, Jr., John E. Mountain of Fame: Portraits in Chinese History (1994) Biographical essays on important figures.
Read more: Maritime on Audiotree Live (Full Session)








