Prince Henry earned his title ‘ the Navigator ’ because he assembled a learn group of designers and maritime experts to design new ships, maps, and navigational instruments. Henry then funded expeditions to use this cognition to sail the High Seas and explore the west african seashore. Building up a massive body of nautical know-how with each expedition, Henry oversaw the beginning stages of a action that gained the Portuguese a global empire .Remove Ads
Advertisement
Early Life & Ceuta
Prince Henry was born in 1394, the third son of John I of Portugal ( aka d. João I, r. 1385-1433 ) and Queen Philippa, who was English. possibly not quite the educated and learned scholar his Renaissance-era caption extolled, Henry was surely a devout Christian. Wearing a hair’s-breadth shirt and dedicating himself to a life of celibacy, Henry did not marry or father any children. His life was dedicated to exploration, empire, and defeating Muslims wherever they were found. He loved pomp and ceremony, the chivalrous code of knights, and he was known for his excessive parties.
Reading: Prince Henry the Navigator
Prince Henry the Navigator charged his team of maritime experts with designing a raw character of ship which could sail both with & against the wreathe .
In 1415, the Portuguese attacked the rich Muslim city of Ceuta in North Africa in a reclamation of Christian-Muslim hostilities. The city was well-fortified, but the Portuguese had let it be known their flit intended to attack the dutch over a deal dispute and so Ceuta was unprepared. The storm had closely 20,000 men, including over 5,000 knights. The king, Prince Henry, and his brothers jointly commanded this extraordinary force out that was attempting to rekindle the flames of the old crusades. Things did not start well. First becalmed, midst fog and irregular winds then split up the armada before it reached its address. When the united states army finally landed, the Portuguese were able to force their way into Ceuta ’ sulfur fortress through diaphanous weight of numbers with Henry in the thick of the carry through. The city fell in a day on 22 August, and a massacre and chaotic round of looting followed .Remove Ads
Advertisement
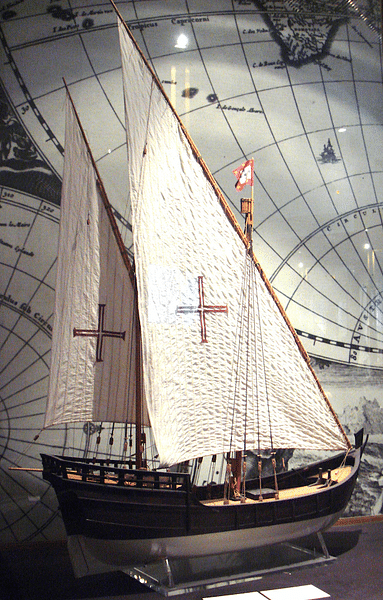
Portuguese Caravel with Lateen Sails
Henry was knighted for his key role in the capture of Ceuta, and he was then made responsible for the defense mechanism of the city by his founder. In 1419-20, the Prince resisted a massive counterattack on the city. Henry used Ceuta as a base from which to launch periodic attacks on the Muslim settlements along the slide – possibly this was the real purpose in capturing the city. Enemy ships in the Mediterranean were ruthlessly sink. In 1415, Henry was made the Duke of Viseu and in 1420, via a papal bullshit, he was appointed the administrator of the Order of Christ, an outgrowth of the now-defunct Knights Templar. Immensely rich thanks to his royal connections and estates, Henry raked in cash from many projects, including a monopoly on the manufacture of soap. This was all very well and satisfied the prince ’ s religious zeal and crave for chivalric enterprise, but he wanted more. He wanted the world .
The Caravel & Lateen Sail
Henry the Navigator was particularly keen for Portugal to be at the forefront of european territorial exploration, to challenge the Islamic caliphates in North Africa and the Middle East, and possibly find the fabled Christian kingdom of the east with a rule called Prester John, most probably somewhere in Ethiopia in East Africa. At Sagres on the southerly tip of Portugal in 1419, Henry assembled a team of experts in mapmaking, navigation, astronomy, mathematics, and ship design. The group included both Christians and Jews, and they were not diffident to use arab sources of information. Contrary to legend, there was no navigational school here. Up to that point, european sweep vessels had depended on either teams of rowers or fixed sails or both for their propulsion ; the square-rigged barca being the most common. The trouble with these square-rigged ships was that they could lone effectively sail with a direct hoist from aft. Love History ?
Sign up for our release weekly electronic mail newsletter !
prince Henry charged his team with designing a new type of transport, one which could sail both with and against the wind and which could explore dangerous unknown rocky shores, inland waterways, and the open ocean. The answer they came up with, based on a type of portuguese fish vessel, was the caravel ( caravela in spanish and portuguese ) .

Bust of Henry the Navigator
The caravel was a type of medium-sized ship which had a shoal draft and lateen or triangular sails. It was debauched, maneuverable, and lone needed a little gang to sail. The early caravels were small and weighed no more than 80 tons, but by and by versions did increase to 100-150 tons. They had a grim rudder, two or three masts, and a classifiable raised forecastle and sterncastle. A caravel had a distinctive length-to-beam proportion of 3.5:1 .Remove Ads
Advertisement
The lateen cruise was a crucial share of the design and of Henry ’ second plans for exploration. The name of this triangular sweep derives from ‘ Latin ’ even if it was inspired by the sails of Arab seafaring vessels, particularly the dhow with its single lateen sweep. elastic lateen sails permitted a vessel to sail within five points off the wind and even to tack ( move in a forward zigzag ) against a headwind .
To gain more cargo space, the caravel design was tweaked to create the round caravel or caravela redonda. This type was larger and wider than a normal caravel and could weigh up to 300 tons. The round caravel normally had square-rigged masts for greater speed and a bowsprit with spritsail. A third gear form was a four-masted caravel designed for function as a warship. typically, three masts carried lateen sails and one was square-rigged .
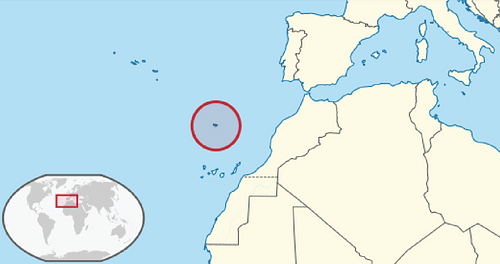
Map Showing the Location of the Madeira Archipelago
Read more: How Maritime Law Works
The First Colony: Madeira
Henry the Navigator then set about fund expeditions using his new ship design, and it brought rewards, even if he himself spent very little meter on water system and none at all on an ocean-going ocean trip. Two captains of vessels sponsored by Prince Henry, who were meant to be raiding the Moroccan coast, landed at Porto Santo in the uninhabited Madeira archipelago during a storm in 1418. The accidental explorers quickly realised the potential of the place – one later sailor described it as “ one large garden ” ( Cliff, 71 ) – and reported back to Henry. In 1419 the portuguese Crown formally declared possession of the North Atlantic island group, located some 800 km ( 500 secret intelligence service ) from the African coast. Governorship of Madeira was awarded to Prince Henry. The portuguese military order, the Order of Christ, whose head was Henry, was granted single rights there. The islands were colonised from 1420, and Henry was directly responsible for the mind of growing carbohydrate cane on the islands, creating a grove system that would finally be copied in colonies elsewhere but specially in portuguese Brazil .Remove Ads
Advertisement
Europeans had long been intrigued by the mind that the heart of Africa contained fabulously deep aureate mines .
The Fall of Ceuta
To balance this success, Prince Henry did have to endure two recurring failures. The inaugural was his try to control the Canary Islands. The armies of Castile and the autochthonal Guanches repelled the Portuguese three times, and Henry had to settle for islands elsewhere. meanwhile, Ceuta proved something of a disappointment, excessively, as the city lost all its trade following occupation. Muslim merchants and trading vessels simply diverted further along the coast to Tangiers. Henry managed to persuade the king to fund another campaign, but Tangiers was much bigger and better defended than Ceuta, and without appropriate siege engines, the excursion proved a blue bankruptcy in 1437. Henry was obliged to hand over his buddy Ferdinand as a hostage in order to permit a portuguese retrograde. part of the deal was to give up Ceuta, but Henry reneged on the agreement, and his buddy died in a Muslim prison. As raids continued on union african ports, the lure of West Africa began to sway the prince ’ s territorial ambitions. Portugal would now focus on the Atlantic .
Rounding Cape Bojador
West Africa offered uncorroborated opportunities, possibly resources of its own but very probable access to trade networks within the interior of that continent which bypassed the Muslims in north African. Ever since Mansa Musa I ( r. 1312 to 1337 ), ruler of the Mali Empire, had visited Cairo in 1324 and wowed everyone with the measure of gold carried by his cortege, Europeans had been intrigued by the estimate that the heart of Africa contained fabulously rich gold mines. A major obstacle to the plan of accessing the region was a geographic matchless : how to sail around Cape Bojador and be able to make it back to Europe against the prevail north winds and unfavorable currents ? It was besides believed by many portuguese sailors and others that the waters beyond the cape were beset with storms, severe fogs, and impossible ocean monsters .
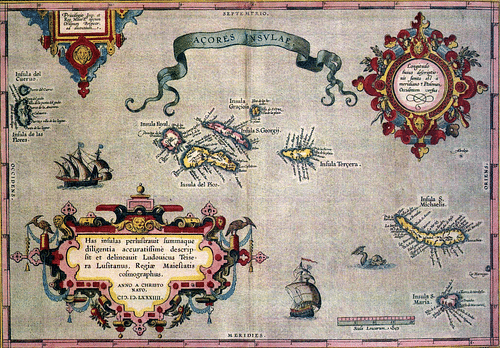
1584 Map of the Azores
Over 12 years, Henry had funded 14 expeditions with the enlistment of italian bankers and the objective to round the cape. Henry ’ s ships all carried white sails emblazoned with the loss crabbed of the Templars, but the emblem did them no good, and all 14 fleets failed in their prey. The lateen caravel was the answer to these problems, along with a good bit of daring. By setting a bold path off from the African coastline and using winds, currents, and hard-hitting areas, the Portuguese found they could safely sail back home plate. The punic Cape Bojador was therefore navigated in 1434 by the portuguese explorer Gil Eannes .Remove Ads
Advertisement
Prince Henry then instructed all subsequent expeditions to cautiously record their experiences. consequently, a invaluable scientific record of winds, tides, currents, and coastlines was built up, and everlastingly accurate charts were drawn of Africa and kept in Lisbon. The Portuguese were notoriously reluctant to share their findings with anyone else, and this nautical information efficaciously became a state secret. There were, besides, additions to zoological cognition. For the beginning clock, Europeans understand where migrant birds flew when they left Europe, countless new species were identified and new peoples encountered .
The Azores & Beyond
The next target on Henry ’ s colonization list was the Azores archipelago ( Açores ) further out in the Atlantic Ocean. The summons of colonization began there in 1439, with overlordship divided between Prince Henry and the regent Prince Pedro, although after the latter ’ south death in 1449, Henry took over the solid archipelago. Both Madeira and the Azores were parcelled up into captaincies for agrarian and trade development, a model that would be copied in many subsequent portuguese colonies as the conglomerate spread from the Americas to East Asia. The Atlantic islands became step stones for voyages that went even further afield, finally around the Cape of Good Hope in southern Africa and beyond to Asia. Prince Henry profited vastly from the resources and trade opportunities this colonization brought to the Portuguese Crown and himself personally .
Exploiting Africa
Henry the Navigator continued to send expeditions to explore the western coast of Africa and extract anything of value. Gold, hides, and some foodstuffs were exchanged for bales of fabric. The quantities were not bang-up but enough for the portuguese crown to begin minting their celebrated upstanding amber mint, the cruzado, from 1457. The year 1444 saw the foremost Portuguese expedition which took slaves from Africa – men, women, and children – after a foray on settlements on Arguin Island. This was the site of the first portuguese feitoria ( fortify trade station ) oversea. 240 slaves captured from this first base raid were paraded naked at the docks of Lisbon. early states had hanker been slave-trading in Africa, but this dockside spectacle was an ill omen of the human calamity to follow in subsequent centuries. The very following year, another and larger slave-hunting dispatch was launched, and others followed so that some 20,000 slaves were brought to Lisbon in the following 15 years. identical quickly, african peoples began to see the bewildering fresh threat to them from these strange visitors with their leftover ashen hide, gleaming armor, and gunpowder weapons .
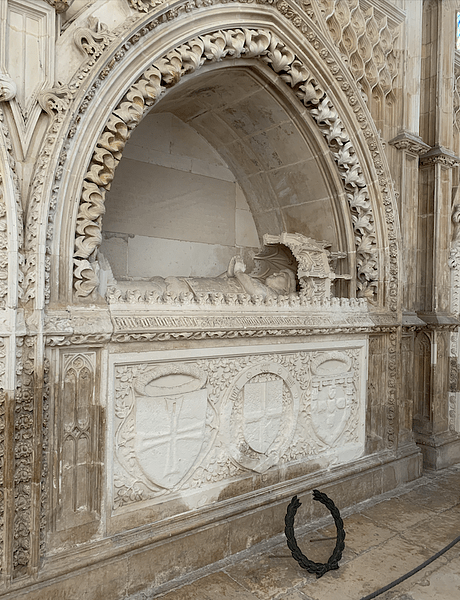
Tomb of Henry the Navigator
Read more: Should You Buy CTRM Stock?
The slave craft brought Henry enrichment and glory. Strange as it seems to us today, Henry was not criticised for this trade but, on the contrary, widely congratulated and applauded for finding a new source of wealth, damaging Islamic barter networks, and giving pagans the opportunity to know the christian faith. These arguments were used to justify colonialism in the minds of those who conducted it for the future 400 years. importantly, the Pope described Henry in a papal bull as “ our beloved son ” and a “ true soldier of Christ ” ( Cliff, 99 ). The ‘Navigator ‘ was at the acme of his fame and baron, but he was, of course, mortal .
Prince Henry died in 1460, and he was given an impressive grave in the Batalha Monastery in central Portugal. He did not, then, live to see the incredible extent of the empire he had begun to forge. More portuguese exploration followed, and more and more colonies joined the Atlantic islands as bantam Portugal wove a web of deal ports across the globe from Brazil to Japan. The chapel service Henry had founded at Belém outside Lisbon remained the last compass point of home that mariners saw before they left Portugal to reach these far-flung colonies. A custom arose that crews would say their prayers in this chapel service on the evening of their departure, asking their god for a successful voyage and a safe refund home. Henry the Navigator, meanwhile, became a fabled figure thanks to his achievements and such late-medieval chronicles of his animation as written by Zurara ( c. 1410 – c. 1474 ). evening in the fifteenth century, some critics did eminence that the prince was preferably excessively interested in wealth and harking back to the long-gone days of the crusades, but he was, however, widely celebrated for centuries as the founding forefather of Portugal ’ s maritime empire .







